VMobject#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.types.vectorized\_mobject.VMobject
- class VMobject(fill_color=None, fill_opacity=0.0, stroke_color=None, stroke_opacity=1.0, stroke_width=4, background_stroke_color='#000000', background_stroke_opacity=1.0, background_stroke_width=0, sheen_factor=0.0, joint_type=None, sheen_direction=array([- 1., 1., 0.]), close_new_points=False, pre_function_handle_to_anchor_scale_factor=0.01, make_smooth_after_applying_functions=False, background_image=None, shade_in_3d=False, tolerance_for_point_equality=1e-06, n_points_per_cubic_curve=4, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
MobjectA vectorized mobject.
- Parameters
background_stroke_color – The purpose of background stroke is to have something that won’t overlap fill, e.g. For text against some textured background.
sheen_factor – When a color c is set, there will be a second color computed based on interpolating c to WHITE by with sheen_factor, and the display will gradient to this secondary color in the direction of sheen_direction.
close_new_points – Indicates that it will not be displayed, but that it should count in parent mobject’s path
tolerance_for_point_equality – This is within a pixel
joint_type (LineJointType | None) – The line joint type used to connect the curve segments of this vectorized mobject. See
LineJointTypefor options.
Methods
add_cubic_bezier_curveAdd cubic bezier curve to the path.
add_cubic_bezier_curvesAdd a straight line from the last point of VMobject to the given point.
add_points_as_cornersAdd Quadratic bezier curve to the path.
Creates a smooth curve from given points and add it to the VMobject.
add_subpathAdds points to self and vmobject so that they both have the same number of subpaths, with corresponding subpaths each containing the same number of points.
align_rgbasappend_pointsappend_vectorized_mobjectapply_functionChanges the anchor mode of the bezier curves.
clear_pointsclose_pathcolor_using_background_imageconsider_points_equalsDetermine if two points are close enough to be considered equal.
fadeMakes sure that points are either directed clockwise or counterclockwise.
Returns the bezier tuples from an array of points.
gen_subpaths_from_points_2dFirst arg can be either a color, or a tuple/list of colors.
Returns the anchors of the curves forming the VMobject.
Returns anchors1, handles1, handles2, anchors2, where (anchors1[i], handles1[i], handles2[i], anchors2[i]) will be four points defining a cubic bezier curve for any i in range(0, len(anchors1))
Return the approximated length of the whole curve.
get_background_imageReturns the color of the
Mobjectget_cubic_bezier_tuplesget_cubic_bezier_tuples_from_pointsGets the functions for the curves of the mobject.
Gets the functions and lengths of the curves for the mobject.
Uses
shoelace_direction()to calculate the direction.Return the end anchors of the bezier curves.
If there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
get_fill_colorsget_fill_opacitiesIf there are multiple opacities, this returns the first
get_fill_rgbasget_gradient_start_and_end_pointsget_group_classget_last_pointReturn the base class of this mobject type.
Returns the expression of the nth curve.
Returns the expression of the nth curve along with its (approximate) length.
Returns the (approximate) length of the nth curve.
Returns the array of short line lengths used for length approximation.
Returns the points defining the nth curve of the vmobject.
Returns the number of curves of the vmobject.
The simplest
Mobjectto be transformed to or from self.get_points_defining_boundaryget_sheen_directionget_sheen_factorReturns the start anchors of the bezier curves.
get_stroke_colorget_stroke_colorsget_stroke_opacitiesget_stroke_opacityget_stroke_rgbasget_stroke_widthget_styleReturns the subcurve of the VMobject between the interval [a, b].
Returns subpaths formed by the curves of the VMobject.
get_subpaths_from_pointshas_new_path_startedInitializes the colors.
Inserts n curves to the bezier curves of the vmobject.
Given an array of k points defining a bezier curves (anchors and handles), returns points defining exactly k + n bezier curves.
interpolate_coloris_closedmake_jaggedmake_smoothmatch_background_imagematch_styleGets the point at a proportion along the path of the
VMobject.Given two bounds a and b, transforms the points of the self vmobject into the points of the vmobject passed as parameter with respect to the bounds.
Returns the proportion along the path of the
VMobjecta particular given point is at.Resize the array of anchor points and handles to have the specified size.
Reverts the point direction by inverting the point order.
Rotates the
Mobjectabout a certain point.Rotates the direction of the applied sheen.
If the distance between a given handle point H and its associated anchor point A is d, then it changes H to be a distances factor*d away from A, but so that the line from A to H doesn't change.
Given two sets of anchors and handles, process them to set them as anchors and handles of the VMobject.
set_background_strokeCondition is function which takes in one arguments, (x, y, z).
Set the fill color and fill opacity of a
VMobject.set_opacityset_pointsGiven an array of points, set them as corner of the vmobject.
set_points_smoothlyset_shade_in_3dApplies a color gradient from a direction.
Sets the direction of the applied sheen.
set_strokeset_stylestart_new_pathupdate_rgbas_arrayAttributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridescolordepthThe depth of the mobject.
If there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorwidthThe width of the mobject.
- add_cubic_bezier_curve_to(handle1, handle2, anchor)[source]#
Add cubic bezier curve to the path.
NOTE : the first anchor is not a parameter as by default the end of the last sub-path!
- Parameters
handle1 (ndarray) – first handle
handle2 (ndarray) – second handle
anchor (ndarray) – anchor
- Returns
self- Return type
- add_line_to(point)[source]#
Add a straight line from the last point of VMobject to the given point.
- Parameters
point (ndarray) – end of the straight line.
- Returns
self- Return type
- add_quadratic_bezier_curve_to(handle, anchor)[source]#
Add Quadratic bezier curve to the path.
- Returns
self- Return type
- Parameters
handle (ndarray) –
anchor (ndarray) –
- add_smooth_curve_to(*points)[source]#
Creates a smooth curve from given points and add it to the VMobject. If two points are passed in, the first is interpreted as a handle, the second as an anchor.
- Parameters
points (array) – Points (anchor and handle, or just anchor) to add a smooth curve from
- Returns
self- Return type
- Raises
ValueError – If 0 or more than 2 points are given.
- align_points(vmobject)[source]#
Adds points to self and vmobject so that they both have the same number of subpaths, with corresponding subpaths each containing the same number of points.
Points are added either by subdividing curves evenly along the subpath, or by creating new subpaths consisting of a single point repeated.
- change_anchor_mode(mode)[source]#
Changes the anchor mode of the bezier curves. This will modify the handles.
There can be only two modes, “jagged”, and “smooth”.
- Returns
self- Return type
- Parameters
mode (str) –
- consider_points_equals_2d(p0, p1)[source]#
Determine if two points are close enough to be considered equal.
This uses the algorithm from np.isclose(), but expanded here for the 2D point case. NumPy is overkill for such a small question. :param p0: first point :param p1: second point
- Returns
whether two points considered close.
- Return type
bool
- Parameters
p0 (ndarray) –
p1 (ndarray) –
- property fill_color#
If there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
- force_direction(target_direction)[source]#
Makes sure that points are either directed clockwise or counterclockwise.
- Parameters
target_direction (str) – Either
"CW"or"CCW".
- gen_cubic_bezier_tuples_from_points(points)[source]#
Returns the bezier tuples from an array of points.
self.points is a list of the anchors and handles of the bezier curves of the mobject (ie [anchor1, handle1, handle2, anchor2, anchor3 ..]) This algorithm basically retrieve them by taking an element every n, where n is the number of control points of the bezier curve.
- Parameters
points (ndarray) – Points from which control points will be extracted.
- Returns
Bezier control points.
- Return type
Tuple
- generate_rgbas_array(color, opacity)[source]#
First arg can be either a color, or a tuple/list of colors. Likewise, opacity can either be a float, or a tuple of floats. If self.sheen_factor is not zero, and only one color was passed in, a second slightly light color will automatically be added for the gradient
- get_anchors()[source]#
Returns the anchors of the curves forming the VMobject.
- Returns
The anchors.
- Return type
np.ndarray
- get_anchors_and_handles()[source]#
Returns anchors1, handles1, handles2, anchors2, where (anchors1[i], handles1[i], handles2[i], anchors2[i]) will be four points defining a cubic bezier curve for any i in range(0, len(anchors1))
- Returns
Iterable of the anchors and handles.
- Return type
Iterable[np.ndarray]
- get_arc_length(sample_points_per_curve=None)[source]#
Return the approximated length of the whole curve.
- Parameters
sample_points_per_curve (int | None) – Number of sample points per curve used to approximate the length. More points result in a better approximation.
- Returns
The length of the
VMobject.- Return type
float
- get_curve_functions()[source]#
Gets the functions for the curves of the mobject.
- Returns
The functions for the curves.
- Return type
Iterable[Callable[[float], np.ndarray]]
- get_curve_functions_with_lengths(**kwargs)[source]#
Gets the functions and lengths of the curves for the mobject.
- Parameters
**kwargs – The keyword arguments passed to
get_nth_curve_function_with_length()- Returns
The functions and lengths of the curves.
- Return type
Iterable[Tuple[Callable[[float], np.ndarray], float]]
- get_direction()[source]#
Uses
shoelace_direction()to calculate the direction. The direction of points determines in which direction the object is drawn, clockwise or counterclockwise.Examples
The default direction of a
Circleis counterclockwise:>>> from manim import Circle >>> Circle().get_direction() 'CCW'
- Returns
Either
"CW"or"CCW".- Return type
str
- get_end_anchors()[source]#
Return the end anchors of the bezier curves.
- Returns
Starting anchors
- Return type
np.ndarray
- get_nth_curve_function(n)[source]#
Returns the expression of the nth curve.
- Parameters
n (int) – index of the desired curve.
- Returns
expression of the nth bezier curve.
- Return type
Callable[float]
- get_nth_curve_function_with_length(n, sample_points=None)[source]#
Returns the expression of the nth curve along with its (approximate) length.
- Parameters
n (int) – The index of the desired curve.
sample_points (int | None) – The number of points to sample to find the length.
- Returns
curve (typing.Callable[[float], np.ndarray]) – The function for the nth curve.
length (
float) – The length of the nth curve.
- Return type
tuple[Callable[[float], np.ndarray], float]
- get_nth_curve_length(n, sample_points=None)[source]#
Returns the (approximate) length of the nth curve.
- Parameters
n (int) – The index of the desired curve.
sample_points (int | None) – The number of points to sample to find the length.
- Returns
length – The length of the nth curve.
- Return type
float
- get_nth_curve_length_pieces(n, sample_points=None)[source]#
Returns the array of short line lengths used for length approximation.
- Parameters
n (int) – The index of the desired curve.
sample_points (int | None) – The number of points to sample to find the length.
- Returns
The short length-pieces of the nth curve.
- Return type
np.ndarray
- get_nth_curve_points(n)[source]#
Returns the points defining the nth curve of the vmobject.
- Parameters
n (int) – index of the desired bezier curve.
- Returns
points defininf the nth bezier curve (anchors, handles)
- Return type
np.ndarray
- get_num_curves()[source]#
Returns the number of curves of the vmobject.
- Returns
number of curves. of the vmobject.
- Return type
int
- get_point_mobject(center=None)[source]#
The simplest
Mobjectto be transformed to or from self. Should by a point of the appropriate type
- get_start_anchors()[source]#
Returns the start anchors of the bezier curves.
- Returns
Starting anchors
- Return type
np.ndarray
- get_subcurve(a, b)[source]#
Returns the subcurve of the VMobject between the interval [a, b]. The curve is a VMobject itself.
- Parameters
a (float) – The lower bound.
b (float) – The upper bound.
- Returns
The subcurve between of [a, b]
- Return type
- get_subpaths()[source]#
Returns subpaths formed by the curves of the VMobject.
Subpaths are ranges of curves with each pair of consecutive curves having their end/start points coincident.
- Returns
subpaths.
- Return type
Tuple
- init_colors(propagate_colors=True)[source]#
Initializes the colors.
Gets called upon creation. This is an empty method that can be implemented by subclasses.
- insert_n_curves(n)[source]#
Inserts n curves to the bezier curves of the vmobject.
- Parameters
n (int) – Number of curves to insert.
- Returns
self- Return type
- insert_n_curves_to_point_list(n, points)[source]#
Given an array of k points defining a bezier curves (anchors and handles), returns points defining exactly k + n bezier curves.
- Parameters
n (int) – Number of desired curves.
points (ndarray) – Starting points.
- Returns
Points generated.
- Return type
np.ndarray
- point_from_proportion(alpha)[source]#
Gets the point at a proportion along the path of the
VMobject.
- pointwise_become_partial(vmobject, a, b)[source]#
Given two bounds a and b, transforms the points of the self vmobject into the points of the vmobject passed as parameter with respect to the bounds. Points here stand for control points of the bezier curves (anchors and handles)
- proportion_from_point(point)[source]#
Returns the proportion along the path of the
VMobjecta particular given point is at.
- resize_points(new_length, resize_func=<function resize_array>)[source]#
Resize the array of anchor points and handles to have the specified size.
- Parameters
new_length (int) – The new (total) number of points.
resize_func (Callable[[ndarray, int], ndarray]) – A function mapping a Numpy array (the points) and an integer (the target size) to a Numpy array. The default implementation is based on Numpy’s
resizefunction.
- reverse_direction()[source]#
Reverts the point direction by inverting the point order.
- Returns
Returns self.
- Return type
Examples
Example: ChangeOfDirection ¶
from manim import * class ChangeOfDirection(Scene): def construct(self): ccw = RegularPolygon(5) ccw.shift(LEFT) cw = RegularPolygon(5) cw.shift(RIGHT).reverse_direction() self.play(Create(ccw), Create(cw), run_time=4)
- rotate(angle, axis=array([0., 0., 1.]), about_point=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Rotates the
Mobjectabout a certain point.- Parameters
angle (float) –
axis (np.ndarray) –
about_point (Sequence[float] | None) –
- rotate_sheen_direction(angle, axis=array([0., 0., 1.]), family=True)[source]#
Rotates the direction of the applied sheen.
- Parameters
angle (float) – Angle by which the direction of sheen is rotated.
axis (ndarray) – Axis of rotation.
Examples
Normal usage:
Circle().set_sheen_direction(UP).rotate_sheen_direction(PI)
See also
- scale_handle_to_anchor_distances(factor)[source]#
If the distance between a given handle point H and its associated anchor point A is d, then it changes H to be a distances factor*d away from A, but so that the line from A to H doesn’t change. This is mostly useful in the context of applying a (differentiable) function, to preserve tangency properties. One would pull all the handles closer to their anchors, apply the function then push them out again.
- Parameters
factor (float) – The factor used for scaling.
- Returns
self- Return type
- set_anchors_and_handles(anchors1, handles1, handles2, anchors2)[source]#
Given two sets of anchors and handles, process them to set them as anchors and handles of the VMobject.
anchors1[i], handles1[i], handles2[i] and anchors2[i] define the i-th bezier curve of the vmobject. There are four hardcoded parameters and this is a problem as it makes the number of points per cubic curve unchangeable from 4 (two anchors and two handles).
- Returns
self- Return type
- Parameters
anchors1 (Sequence[float]) –
handles1 (Sequence[float]) –
handles2 (Sequence[float]) –
anchors2 (Sequence[float]) –
- set_color(color, family=True)[source]#
Condition is function which takes in one arguments, (x, y, z). Here it just recurses to submobjects, but in subclasses this should be further implemented based on the the inner workings of color
- set_fill(color=None, opacity=None, family=True)[source]#
Set the fill color and fill opacity of a
VMobject.- Parameters
- Returns
self- Return type
Examples
Example: SetFill ¶
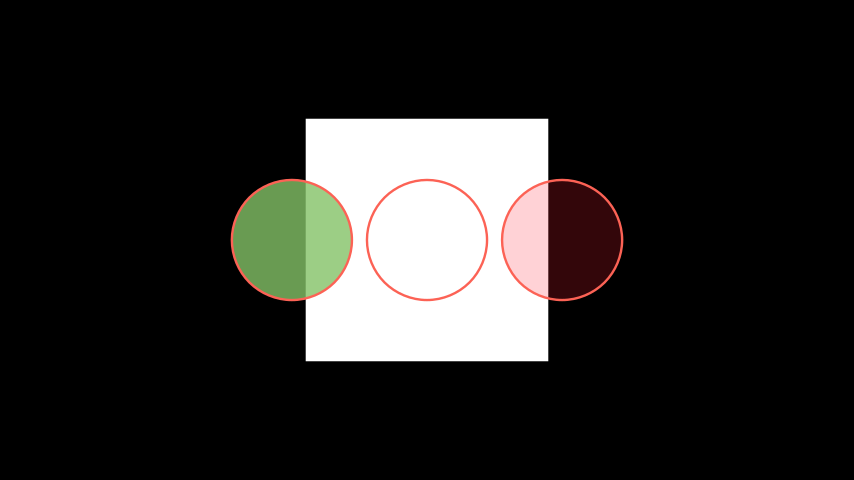
from manim import * class SetFill(Scene): def construct(self): square = Square().scale(2).set_fill(WHITE,1) circle1 = Circle().set_fill(GREEN,0.8) circle2 = Circle().set_fill(YELLOW) # No fill_opacity circle3 = Circle().set_fill(color = '#FF2135', opacity = 0.2) group = Group(circle1,circle2,circle3).arrange() self.add(square) self.add(group)
See also
set_style()
- set_points_as_corners(points)[source]#
Given an array of points, set them as corner of the vmobject.
To achieve that, this algorithm sets handles aligned with the anchors such that the resultant bezier curve will be the segment between the two anchors.
- Parameters
points (Sequence[float]) – Array of points that will be set as corners.
- Returns
self- Return type
- set_sheen(factor, direction=None, family=True)[source]#
Applies a color gradient from a direction.
- Parameters
factor (float) – The extent of lustre/gradient to apply. If negative, the gradient starts from black, if positive the gradient starts from white and changes to the current color.
direction (Optional[ndarray]) – Direction from where the gradient is applied.
Examples
Example: SetSheen ¶

from manim import * class SetSheen(Scene): def construct(self): circle = Circle(fill_opacity=1).set_sheen(-0.3, DR) self.add(circle)