Angle#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.geometry.line.Angle
- class Angle(line1, line2, radius=None, quadrant=(1, 1), other_angle=False, dot=False, dot_radius=None, dot_distance=0.55, dot_color='#FFFFFF', elbow=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
VMobjectA circular arc or elbow-type mobject representing an angle of two lines.
- Parameters
line1 (Line) – The first line.
line2 (Line) – The second line.
radius (float) – The radius of the
Arc.quadrant (Sequence[int]) – A sequence of two
intnumbers determining which of the 4 quadrants should be used. The first value indicates whether to anchor the arc on the first line closer to the end point (1) or start point (-1), and the second value functions similarly for the end (1) or start (-1) of the second line. Possibilities: (1,1), (-1,1), (1,-1), (-1,-1).other_angle (bool) – Toggles between the two possible angles defined by two points and an arc center. If set to False (default), the arc will always go counterclockwise from the point on line1 until the point on line2 is reached. If set to True, the angle will go clockwise from line1 to line2.
dot (bool) – Allows for a
Dotin the arc. Mainly used as an convention to indicate a right angle. The dot can be customized in the next three parameters.dot_radius (float | None) – The radius of the
Dot. If not specified otherwise, this radius will be 1/10 of the arc radius.dot_distance (float) – Relative distance from the center to the arc: 0 puts the dot in the center and 1 on the arc itself.
dot_color (Colors) – The color of the
Dot.elbow (bool) – Produces an elbow-type mobject indicating a right angle, see
RightAnglefor more information and a shorthand.**kwargs – Further keyword arguments that are passed to the constructor of
ArcorElbow.
Examples
The first example shows some right angles with a dot in the middle while the second example shows all 8 possible angles defined by two lines.
Example: RightArcAngleExample ¶
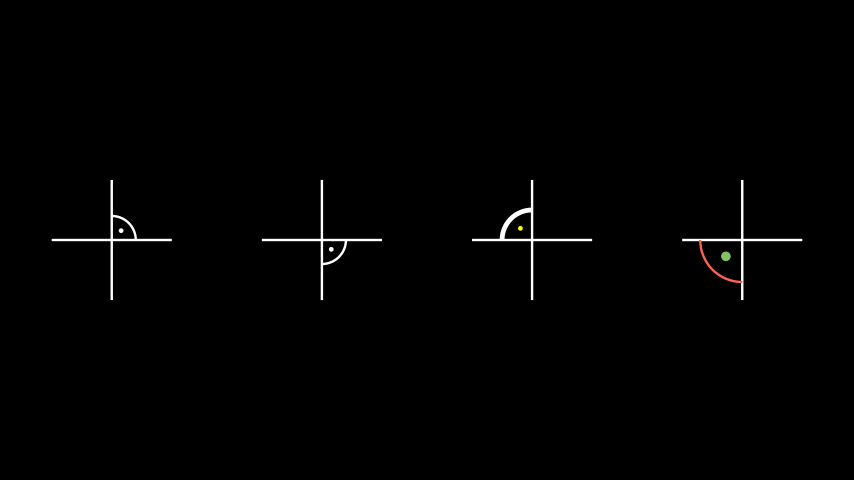
from manim import * class RightArcAngleExample(Scene): def construct(self): line1 = Line( LEFT, RIGHT ) line2 = Line( DOWN, UP ) rightarcangles = [ Angle(line1, line2, dot=True), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.4, quadrant=(1,-1), dot=True, other_angle=True), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.5, quadrant=(-1,1), stroke_width=8, dot=True, dot_color=YELLOW, dot_radius=0.04, other_angle=True), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.7, quadrant=(-1,-1), color=RED, dot=True, dot_color=GREEN, dot_radius=0.08), ] plots = VGroup() for angle in rightarcangles: plot=VGroup(line1.copy(),line2.copy(), angle) plots.add(plot) plots.arrange(buff=1.5) self.add(plots)
Example: AngleExample ¶
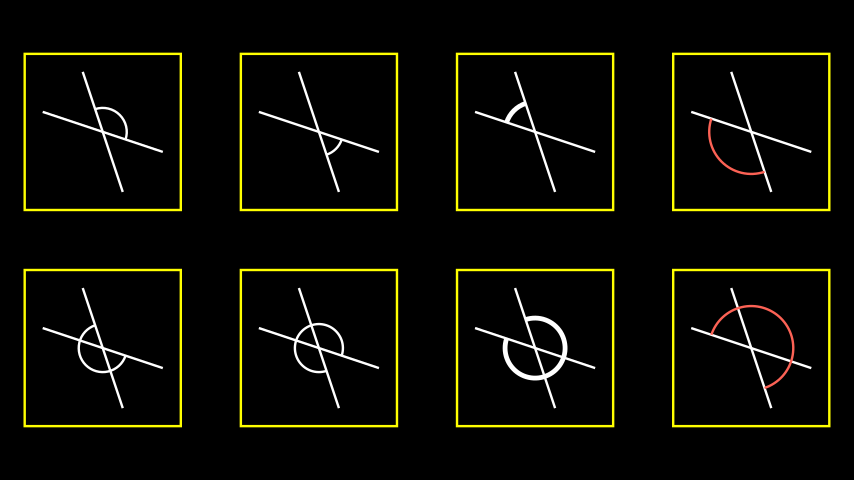
from manim import * class AngleExample(Scene): def construct(self): line1 = Line( LEFT + (1/3) * UP, RIGHT + (1/3) * DOWN ) line2 = Line( DOWN + (1/3) * RIGHT, UP + (1/3) * LEFT ) angles = [ Angle(line1, line2), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.4, quadrant=(1,-1), other_angle=True), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.5, quadrant=(-1,1), stroke_width=8, other_angle=True), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.7, quadrant=(-1,-1), color=RED), Angle(line1, line2, other_angle=True), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.4, quadrant=(1,-1)), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.5, quadrant=(-1,1), stroke_width=8), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.7, quadrant=(-1,-1), color=RED, other_angle=True), ] plots = VGroup() for angle in angles: plot=VGroup(line1.copy(),line2.copy(), angle) plots.add(VGroup(plot,SurroundingRectangle(plot, buff=0.3))) plots.arrange_in_grid(rows=2,buff=1) self.add(plots)
Example: FilledAngle ¶
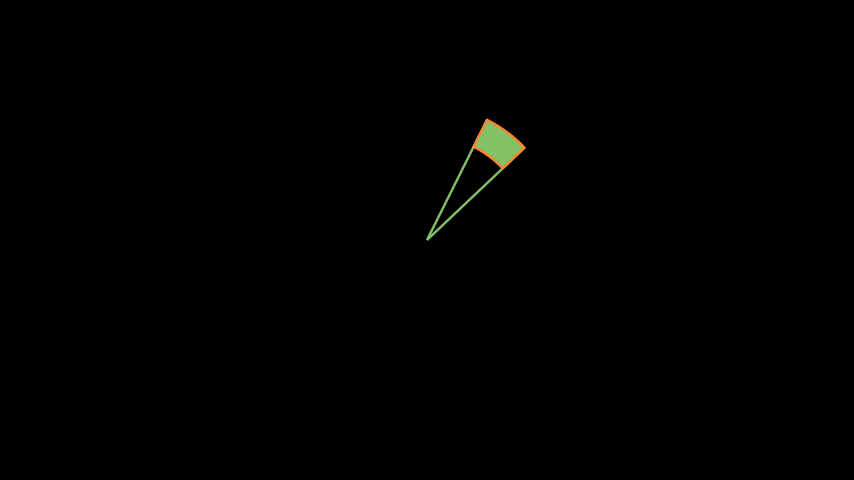
from manim import * class FilledAngle(Scene): def construct(self): l1 = Line(ORIGIN, 2 * UP + RIGHT).set_color(GREEN) l2 = ( Line(ORIGIN, 2 * UP + RIGHT) .set_color(GREEN) .rotate(-20 * DEGREES, about_point=ORIGIN) ) norm = l1.get_length() a1 = Angle(l1, l2, other_angle=True, radius=norm - 0.5).set_color(GREEN) a2 = Angle(l1, l2, other_angle=True, radius=norm).set_color(GREEN) q1 = a1.points # save all coordinates of points of angle a1 q2 = a2.reverse_direction().points # save all coordinates of points of angle a1 (in reversed direction) pnts = np.concatenate([q1, q2, q1[0].reshape(1, 3)]) # adds points and ensures that path starts and ends at same point mfill = VMobject().set_color(ORANGE) mfill.set_points_as_corners(pnts).set_fill(GREEN, opacity=1) self.add(l1, l2) self.add(mfill)
Methods
The angle between the lines AB and BC.
Get the lines forming an angle of the
Angleclass.Get the value of an angle of the
Angleclass.Attributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridescolordepthThe depth of the mobject.
fill_colorIf there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorwidthThe width of the mobject.
- static from_three_points(A, B, C, **kwargs)[source]#
The angle between the lines AB and BC.
This constructs the angle \(\angle ABC\).
- Parameters
A (ndarray) – The endpoint of the first angle leg
B (ndarray) – The vertex of the angle
C (ndarray) – The endpoint of the second angle leg
**kwargs – Further keyword arguments are passed to
Angle
- Returns
Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.5, quadrant=(-1,1), stroke_width=8), Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.7, quadrant=(-1,-1), color=RED, other_angle=True),
- Return type
The Angle calculated from the three points
Examples
Example: AngleFromThreePointsExample ¶

from manim import * class AngleFromThreePointsExample(Scene): def construct(self): sample_angle = Angle.from_three_points(UP, ORIGIN, LEFT) red_angle = Angle.from_three_points(LEFT + UP, ORIGIN, RIGHT, radius=.8, quadrant=(-1,-1), color=RED, stroke_width=8, other_angle=True) self.add(red_angle, sample_angle)
- get_lines()[source]#
Get the lines forming an angle of the
Angleclass.Examples
>>> line_1, line_2 = Line(ORIGIN, RIGHT), Line(ORIGIN, UR) >>> angle = Angle(line_1, line_2) >>> angle.get_lines() VGroup(Line, Line)
- get_value(degrees=False)[source]#
Get the value of an angle of the
Angleclass.- Parameters
degrees (bool) – A boolean to decide the unit (deg/rad) in which the value of the angle is returned.
- Returns
The value in degrees/radians of an angle of the
Angleclass.- Return type
float
Examples
Example: GetValueExample ¶

from manim import * class GetValueExample(Scene): def construct(self): line1 = Line(LEFT+(1/3)*UP, RIGHT+(1/3)*DOWN) line2 = Line(DOWN+(1/3)*RIGHT, UP+(1/3)*LEFT) angle = Angle(line1, line2, radius=0.4) value = DecimalNumber(angle.get_value(degrees=True), unit="^{\circ}") value.next_to(angle, UR) self.add(line1, line2, angle, value)