ArrowTip#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.geometry.tips.ArrowTip
- class ArrowTip(*args, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
VMobjectBase class for arrow tips.
See also
ArrowTriangleTipArrowTriangleFilledTipArrowCircleTipArrowCircleFilledTipArrowSquareTipArrowSquareFilledTipStealthTipExamples
Cannot be used directly, only intended for inheritance:
>>> tip = ArrowTip() Traceback (most recent call last): ... NotImplementedError: Has to be implemented in inheriting subclasses.
Instead, use one of the pre-defined ones, or make a custom one like this:
Example: CustomTipExample ¶
from manim import * >>> from manim import RegularPolygon, Arrow >>> class MyCustomArrowTip(ArrowTip, RegularPolygon): ... def __init__(self, length=0.35, **kwargs): ... RegularPolygon.__init__(self, n=5, **kwargs) ... self.width = length ... self.stretch_to_fit_height(length) >>> arr = Arrow(np.array([-2, -2, 0]), np.array([2, 2, 0]), ... tip_shape=MyCustomArrowTip) >>> isinstance(arr.tip, RegularPolygon) True >>> from manim import Scene, Create >>> class CustomTipExample(Scene): ... def construct(self): ... self.play(Create(arr))
Using a class inherited from
ArrowTipto get a non-filled tip is a shorthand to manually specifying the arrow tip style as follows:>>> arrow = Arrow(np.array([0, 0, 0]), np.array([1, 1, 0]), ... tip_style={'fill_opacity': 0, 'stroke_width': 3})
The following example illustrates the usage of all of the predefined arrow tips.
Example: ArrowTipsShowcase ¶
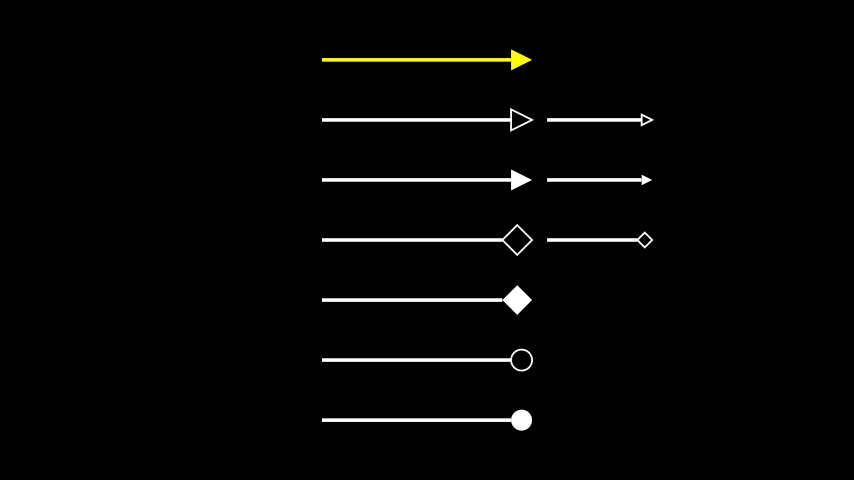
from manim import * from manim.mobject.geometry.tips import ArrowTriangleTip,\ ArrowSquareTip, ArrowSquareFilledTip,\ ArrowCircleTip, ArrowCircleFilledTip class ArrowTipsShowcase(Scene): def construct(self): a00 = Arrow(start=[-2, 3, 0], end=[2, 3, 0], color=YELLOW) a11 = Arrow(start=[-2, 2, 0], end=[2, 2, 0], tip_shape=ArrowTriangleTip) a12 = Arrow(start=[-2, 1, 0], end=[2, 1, 0]) a21 = Arrow(start=[-2, 0, 0], end=[2, 0, 0], tip_shape=ArrowSquareTip) a22 = Arrow([-2, -1, 0], [2, -1, 0], tip_shape=ArrowSquareFilledTip) a31 = Arrow([-2, -2, 0], [2, -2, 0], tip_shape=ArrowCircleTip) a32 = Arrow([-2, -3, 0], [2, -3, 0], tip_shape=ArrowCircleFilledTip) b11 = a11.copy().scale(0.5, scale_tips=True).next_to(a11, RIGHT) b12 = a12.copy().scale(0.5, scale_tips=True).next_to(a12, RIGHT) b21 = a21.copy().scale(0.5, scale_tips=True).next_to(a21, RIGHT) self.add(a00, a11, a12, a21, a22, a31, a32, b11, b12, b21)
Methods
Attributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridesThe base point of the arrow tip.
colordepthThe depth of the mobject.
fill_colorIf there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
The length of the arrow tip.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorThe angle of the arrow tip.
The tip point of the arrow tip.
The vector pointing from the base point to the tip point.
widthThe width of the mobject.
- property base#
The base point of the arrow tip.
This is the point connecting to the arrow line.
Examples
>>> from manim import Arrow >>> arrow = Arrow(np.array([0, 0, 0]), np.array([2, 0, 0]), buff=0) >>> arrow.tip.base.round(2) + 0. # add 0. to avoid negative 0 in output array([1.65, 0. , 0. ])
- property length#
The length of the arrow tip.
Examples
>>> from manim import Arrow >>> arrow = Arrow(np.array([0, 0, 0]), np.array([1, 2, 0])) >>> round(arrow.tip.length, 3) 0.35
- property tip_angle#
The angle of the arrow tip.
Examples
>>> from manim import Arrow >>> arrow = Arrow(np.array([0, 0, 0]), np.array([1, 1, 0]), buff=0) >>> round(arrow.tip.tip_angle, 5) == round(PI/4, 5) True
- property tip_point#
The tip point of the arrow tip.
Examples
>>> from manim import Arrow >>> arrow = Arrow(np.array([0, 0, 0]), np.array([2, 0, 0]), buff=0) >>> arrow.tip.tip_point.round(2) + 0. array([2., 0., 0.])
- property vector#
The vector pointing from the base point to the tip point.
Examples
>>> from manim import Arrow >>> arrow = Arrow(np.array([0, 0, 0]), np.array([2, 2, 0]), buff=0) >>> arrow.tip.vector.round(2) + 0. array([0.25, 0.25, 0. ])