BarChart#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.graphing.probability.BarChart
- class BarChart(values, bar_names=None, y_range=None, x_length=None, y_length=None, bar_colors=['#003f5c', '#58508d', '#bc5090', '#ff6361', '#ffa600'], bar_width=0.6, bar_fill_opacity=0.7, bar_stroke_width=3, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
AxesCreates a bar chart. Inherits from
Axes, so it shares its methods and attributes. Each axis inherits fromNumberLine, so pass inx_axis_config/y_axis_configto control their attributes.- Parameters
values (MutableSequence[float]) – A sequence of values that determines the height of each bar. Accepts negative values.
bar_names (Sequence[str] | None) – A sequence of names for each bar. Does not have to match the length of
values.y_range (Sequence[float] | None) – The y_axis range of values. If
None, the range will be calculated based on the min/max ofvaluesand the step will be calculated based ony_length.x_length (float | None) – The length of the x-axis. If
None, it is automatically calculated based on the number of values and the width of the screen.y_length (float | None) – The length of the y-axis.
bar_colors (Iterable[str]) – The color for the bars. Accepts a sequence of colors (can contain just one item). If the length of``bar_colors`` does not match that of
values, intermediate colors will be automatically determined.bar_width (float) – The length of a bar. Must be between 0 and 1.
bar_fill_opacity (float) – The fill opacity of the bars.
bar_stroke_width (float) – The stroke width of the bars.
Examples
Example: BarChartExample ¶
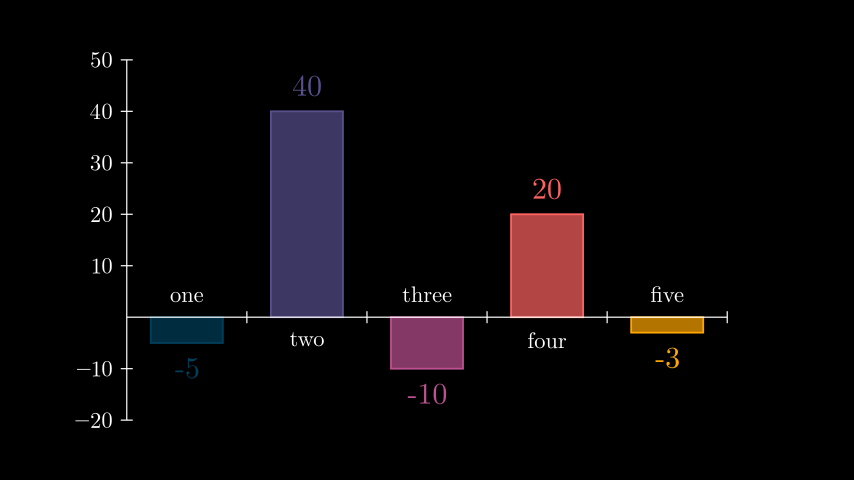
from manim import * class BarChartExample(Scene): def construct(self): chart = BarChart( values=[-5, 40, -10, 20, -3], bar_names=["one", "two", "three", "four", "five"], y_range=[-20, 50, 10], y_length=6, x_length=10, x_axis_config={"font_size": 36}, ) c_bar_lbls = chart.get_bar_labels(font_size=48) self.add(chart, c_bar_lbls)
Methods
Updates the height of the bars of the chart.
Annotates each bar with its corresponding value.
Attributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridescolordepthThe depth of the mobject.
fill_colorIf there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorwidthThe width of the mobject.
- change_bar_values(values, update_colors=True)[source]#
Updates the height of the bars of the chart.
- Parameters
values (Iterable[float]) – The values that will be used to update the height of the bars. Does not have to match the number of bars.
update_colors (bool) – Whether to re-initalize the colors of the bars based on
self.bar_colors.
Examples
Example: ChangeBarValuesExample ¶
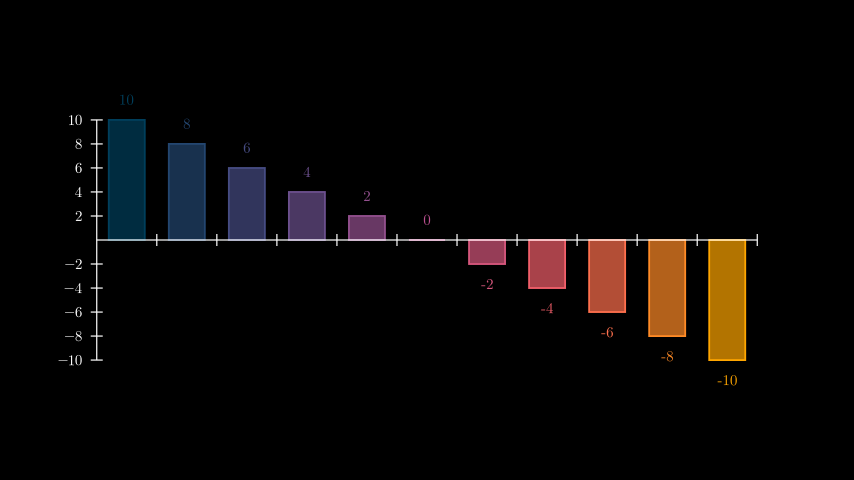
from manim import * class ChangeBarValuesExample(Scene): def construct(self): values=[-10, -8, -6, -4, -2, 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10] chart = BarChart( values, y_range=[-10, 10, 2], y_axis_config={"font_size": 24}, ) self.add(chart) chart.change_bar_values(list(reversed(values))) self.add(chart.get_bar_labels(font_size=24))
- get_bar_labels(color=None, font_size=24, buff=0.25, label_constructor=<class 'manim.mobject.text.tex_mobject.Tex'>)[source]#
Annotates each bar with its corresponding value. Use
self.bar_labelsto access the labels after creation.- Parameters
color (Color | None) – The color of each label. By default
Noneand is based on the parent’s bar color.font_size (float) – The font size of each label.
buff (float) – The distance from each label to its bar. By default 0.4.
label_constructor (type[VMobject]) – The Mobject class to construct the labels, by default
Tex.
Examples
Example: GetBarLabelsExample ¶
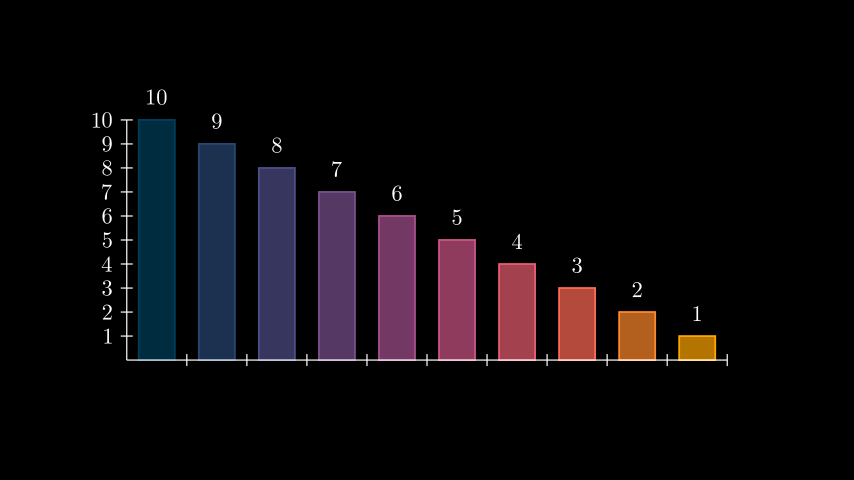
from manim import * class GetBarLabelsExample(Scene): def construct(self): chart = BarChart(values=[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], y_range=[0, 10, 1]) c_bar_lbls = chart.get_bar_labels( color=WHITE, label_constructor=MathTex, font_size=36 ) self.add(chart, c_bar_lbls)