ParametricFunction#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.graphing.functions.ParametricFunction
- class ParametricFunction(function, t_range=None, scaling=<manim.mobject.graphing.scale.LinearBase object>, dt=1e-08, discontinuities=None, use_smoothing=True, use_vectorized=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
VMobjectA parametric curve.
- Parameters
function (Callable[[float, float], float]) – The function to be plotted in the form of
(lambda x: x**2)t_range (Sequence[float] | None) – Determines the length that the function spans. By default
[0, 1]scaling (_ScaleBase) – Scaling class applied to the points of the function. Default of
LinearBase.use_smoothing (bool) – Whether to interpolate between the points of the function after they have been created. (Will have odd behaviour with a low number of points)
use_vectorized (bool) – Whether to pass in the generated t value array to the function as
[t_0, t_1, ...]. Only use this if your function supports it. Output should be a numpy array of shape[[x_0, x_1, ...], [y_0, y_1, ...], [z_0, z_1, ...]]butzcan also be 0 if the Axes is 2Ddiscontinuities (Iterable[float] | None) – Values of t at which the function experiences discontinuity.
dt (float) – The left and right tolerance for the discontinuities.
Examples
Example: PlotParametricFunction ¶
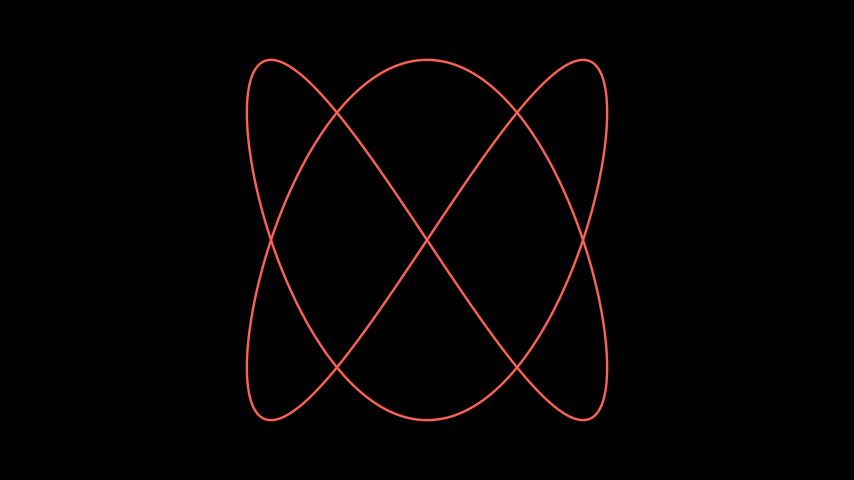
from manim import * class PlotParametricFunction(Scene): def func(self, t): return np.array((np.sin(2 * t), np.sin(3 * t), 0)) def construct(self): func = ParametricFunction(self.func, t_range = np.array([0, TAU]), fill_opacity=0).set_color(RED) self.add(func.scale(3))
Example: ThreeDParametricSpring ¶
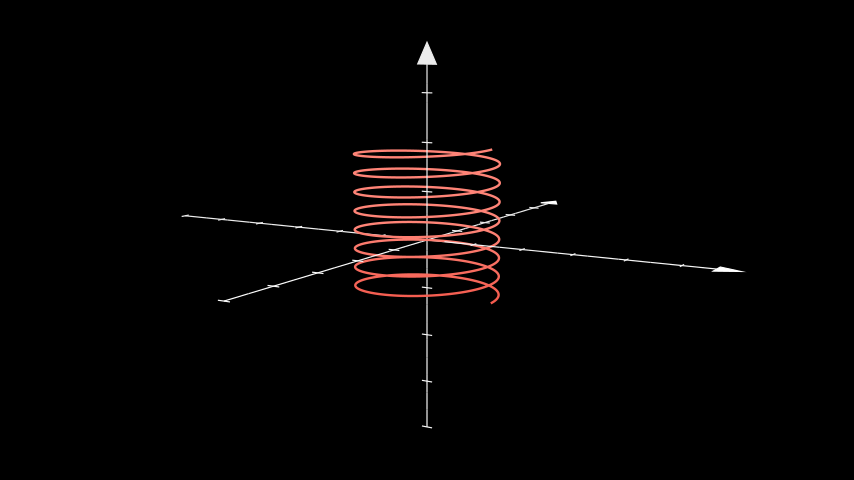
from manim import * class ThreeDParametricSpring(ThreeDScene): def construct(self): curve1 = ParametricFunction( lambda u: np.array([ 1.2 * np.cos(u), 1.2 * np.sin(u), u * 0.05 ]), color=RED, t_range = np.array([-3*TAU, 5*TAU, 0.01]) ).set_shade_in_3d(True) axes = ThreeDAxes() self.add(axes, curve1) self.set_camera_orientation(phi=80 * DEGREES, theta=-60 * DEGREES) self.wait()
Attention
If your function has discontinuities, you’ll have to specify the location of the discontinuities manually. See the following example for guidance.
Example: DiscontinuousExample ¶
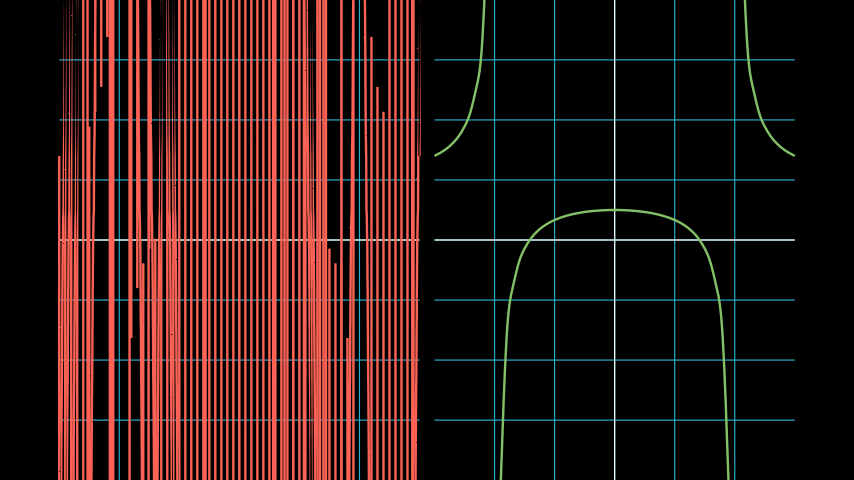
from manim import * class DiscontinuousExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax1 = NumberPlane((-3, 3), (-4, 4)) ax2 = NumberPlane((-3, 3), (-4, 4)) VGroup(ax1, ax2).arrange() discontinuous_function = lambda x: (x ** 2 - 2) / (x ** 2 - 4) incorrect = ax1.plot(discontinuous_function, color=RED) correct = ax2.plot( discontinuous_function, discontinuities=[-2, 2], # discontinuous points dt=0.1, # left and right tolerance of discontinuity color=GREEN, ) self.add(ax1, ax2, incorrect, correct)
Methods
Initializes
pointsand therefore the shape.get_functionget_point_from_functionInitializes
pointsand therefore the shape.Attributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridescolordepthThe depth of the mobject.
fill_colorIf there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorwidthThe width of the mobject.
- generate_points()[source]#
Initializes
pointsand therefore the shape.Gets called upon creation. This is an empty method that can be implemented by subclasses.
- init_points()#
Initializes
pointsand therefore the shape.Gets called upon creation. This is an empty method that can be implemented by subclasses.