Mobject#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.mobject.Mobject
- class Mobject(color='#FFFFFF', name=None, dim=3, target=None, z_index=0)[source]#
Bases:
objectMathematical Object: base class for objects that can be displayed on screen.
There is a compatibility layer that allows for getting and setting generic attributes with
get_*andset_*methods. Seeset()for more details.Methods
Add mobjects as submobjects.
Add an animation override.
Add a BackgroundRectangle as submobject.
add_background_rectangle_to_family_members_with_pointsadd_background_rectangle_to_submobjectsadd_n_more_submobjectsAdd all passed mobjects to the back of the submobjects.
Add an update function to this mobject.
Aligns the data of this mobject with another mobject.
Direction just needs to be a vector pointing towards side or corner in the 2d plane.
align_pointsalign_points_with_largeralign_submobjectsAligns mobject to another
Mobjectin a certain direction.Returns the function defining a specific animation override for this class.
Applies a complex function to a
Mobject.apply_functionapply_function_to_positionapply_function_to_submobject_positionsapply_matrixapply_over_attr_arraysapply_points_function_about_pointApply a function to
selfand every submobject with points recursively.Sorts
Mobjectnext to each other on screen.Arrange submobjects in a grid.
Arrange the position of
submobjectswith a small buffer.Edit points, colors and submobjects to be identical to another
MobjectcenterRemove every updater.
Create and return an identical copy of the
Mobjectincluding allsubmobjects.fadefade_tofamily_members_with_pointsFlips/Mirrors an mobject about its center.
Initializes
pointsand therefore the shape.generate_targetReturn all points from this mobject and all submobjects.
get_array_attrsGet bottom coordinates of a box bounding the
Mobjectget_boundary_pointGet center coordinates
get_center_of_massReturns the color of the
MobjectMeant to generalize
get_x,get_yandget_zGet corner coordinates for certain direction.
Picture a box bounding the
Mobject.Get edge coordinates for certain direction.
Returns the point, where the stroke that surrounds the
Mobjectends.get_extremum_along_dimget_familyget_family_updatersget_group_classget_imageGet left coordinates of a box bounding the
MobjectReturn all of a given attribute from this mobject and all submobjects.
Get coordinates of the middle of the path that forms the
Mobject.Return the base class of this mobject type.
Get nadir (opposite the zenith) coordinates of a box bounding a 3D
Mobject.get_num_pointsget_piecesThe simplest
Mobjectto be transformed to or from self.get_points_defining_boundaryGet right coordinates of a box bounding the
MobjectReturns the point, where the stroke that surrounds the
Mobjectstarts.Returns starting and ending point of a stroke as a
tuple.Return all updaters using the
dtparameter.Get top coordinates of a box bounding the
MobjectReturn all updaters.
Returns x coordinate of the center of the
MobjectasfloatReturns y coordinate of the center of the
MobjectasfloatReturns z coordinate of the center of the
Mobjectasfloatget_z_index_reference_pointGet zenith coordinates of a box bounding a 3D
Mobject.Check if
Mobjectdoes not contains points.Check if
Mobjectcontains points.Test if
selfhas a time based updater.Initializes the colors.
Inserts a mobject at a specific position into self.submobjects
Turns this
Mobjectinto an interpolation betweenmobject1andmobject2.interpolate_colorInverts the list of
submobjects.is_off_screenMeasure the length of an
Mobjectin a certain direction.Match the color with the color of another
Mobject.Match the coordinates with the coordinates of another
Mobject.Match the depth with the depth of another
Mobject.Match the specified dimension with the dimension of another
Mobject.Match the height with the height of another
Mobject.Edit points, positions, and submobjects to be identical to another
Mobject, while keeping the style unchanged.Match the updaters of the given mobject.
Match the width with the width of another
Mobject.Match x coord.
Match y coord.
Match z coord.
Move center of the
Mobjectto certain coordinate.nonempty_submobjectsIf a
Mobjectwith points is being aligned to one without, treat both as groups, and push the one with points into its own submobjects list.point_from_proportionpose_at_angleproportion_from_pointpush_self_into_submobjectsput_start_and_end_onFind the min or max value from a dimension across all points in this and submobjects.
Remove
submobjects.Remove an updater.
This can make transition animations nicer
repeat_submobjectreplacerescale_to_fitSets
pointsto be an empty array.Restores the state that was previously saved with
save_state().Enable updating from updaters and animations.
reverse_pointsRotates the
Mobjectabout a certain point.Rotates the
Mobjectabout the ORIGIN, which is at [0,0,0].Saves an image of only this
Mobjectat its position to a png file.Save the current state (position, color & size).
Scale the size by a factor.
Scales the
Mobjectto fit a depth while keeping width/height proportional.Scales the
Mobjectto fit a height while keeping width/depth proportional.Scales the
Mobjectto fit a width while keeping height/depth proportional.Sets attributes.
Condition is function which takes in one arguments, (x, y, z).
set_color_by_gradientset_colors_by_radial_gradientset_coordSets the default values of keyword arguments.
set_submobject_colors_by_gradientset_submobject_colors_by_radial_gradientSet x value of the center of the
Mobject(intorfloat)Set y value of the center of the
Mobject(intorfloat)Set z value of the center of the
Mobject(intorfloat)Sets the
Mobject'sz_indexto the value specified in z_index_value.Sets the
Mobject's z coordinate to the value ofz_index.Shift by the given vectors.
shift_onto_screenshowShuffles the list of
submobjects.Shuffles the order of
submobjectsSorts the list of
submobjectsby a function defined bysubmob_func.Sort the
submobjectsspace_out_submobjectssplitstretchstretch_about_pointStretches the
Mobjectto fit a depth, not keeping width/height proportional.Stretches the
Mobjectto fit a height, not keeping width/depth proportional.Stretches the
Mobjectto fit a width, not keeping height/depth proportional.surroundDisable updating from updaters and animations.
throw_error_if_no_pointsto_cornerto_edgeto_original_colorApply all updaters.
wagAttributes
Used to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridesThe depth of the mobject.
The height of the mobject.
The width of the mobject.
- add(*mobjects)[source]#
Add mobjects as submobjects.
The mobjects are added to
submobjects.Subclasses of mobject may implement
+and+=dunder methods.- Parameters
mobjects (Mobject) – The mobjects to add.
- Returns
self- Return type
- Raises
ValueError – When a mobject tries to add itself.
TypeError – When trying to add an object that is not an instance of
Mobject.
Notes
A mobject cannot contain itself, and it cannot contain a submobject more than once. If the parent mobject is displayed, the newly-added submobjects will also be displayed (i.e. they are automatically added to the parent Scene).
See also
Examples
>>> outer = Mobject() >>> inner = Mobject() >>> outer = outer.add(inner)
Duplicates are not added again:
>>> outer = outer.add(inner) >>> len(outer.submobjects) 1
Adding an object to itself raises an error:
>>> outer.add(outer) Traceback (most recent call last): ... ValueError: Mobject cannot contain self
A given mobject cannot be added as a submobject twice to some parent:
>>> parent = Mobject(name="parent") >>> child = Mobject(name="child") >>> parent.add(child, child) [...] WARNING ... parent >>> parent.submobjects [child]
- classmethod add_animation_override(animation_class, override_func)[source]#
Add an animation override.
This does not apply to subclasses.
- Parameters
- Raises
MultiAnimationOverrideException – If the overridden animation was already overridden.
- add_background_rectangle(color=None, opacity=0.75, **kwargs)[source]#
Add a BackgroundRectangle as submobject.
The BackgroundRectangle is added behind other submobjects.
This can be used to increase the mobjects visibility in front of a noisy background.
- Parameters
color (Colors | None) – The color of the BackgroundRectangle
opacity (float) – The opacity of the BackgroundRectangle
kwargs – Additional keyword arguments passed to the BackgroundRectangle constructor
- Returns
self- Return type
See also
- add_to_back(*mobjects)[source]#
Add all passed mobjects to the back of the submobjects.
If
submobjectsalready contains the given mobjects, they just get moved to the back instead.Note
Technically, this is done by adding (or moving) the mobjects to the head of
submobjects. The head of this list is rendered first, which places the corresponding mobjects behind the subsequent list members.- Raises
ValueError – When a mobject tries to add itself.
TypeError – When trying to add an object that is not an instance of
Mobject.
- Parameters
mobjects (Mobject) –
Notes
A mobject cannot contain itself, and it cannot contain a submobject more than once. If the parent mobject is displayed, the newly-added submobjects will also be displayed (i.e. they are automatically added to the parent Scene).
- add_updater(update_function, index=None, call_updater=False)[source]#
Add an update function to this mobject.
Update functions, or updaters in short, are functions that are applied to the Mobject in every frame.
- Parameters
update_function (Updater) – The update function to be added. Whenever
update()is called, this update function gets called usingselfas the first parameter. The updater can have a second parameterdt. If it uses this parameter, it gets called using a second valuedt, usually representing the time in seconds since the last call ofupdate().index (int | None) – The index at which the new updater should be added in
self.updaters. In caseindexisNonethe updater will be added at the end.call_updater (bool) – Whether or not to call the updater initially. If
True, the updater will be called usingdt=0.
- Returns
self- Return type
Examples
Example: NextToUpdater ¶
from manim import * class NextToUpdater(Scene): def construct(self): def dot_position(mobject): mobject.set_value(dot.get_center()[0]) mobject.next_to(dot) dot = Dot(RIGHT*3) label = DecimalNumber() label.add_updater(dot_position) self.add(dot, label) self.play(Rotating(dot, about_point=ORIGIN, angle=TAU, run_time=TAU, rate_func=linear))
Example: DtUpdater ¶
from manim import * class DtUpdater(Scene): def construct(self): line = Square() #Let the line rotate 90° per second line.add_updater(lambda mobject, dt: mobject.rotate(dt*90*DEGREES)) self.add(line) self.wait(2)
See also
- align_data(mobject, skip_point_alignment=False)[source]#
Aligns the data of this mobject with another mobject.
Afterwards, the two mobjects will have the same number of submobjects (see
align_submobjects()), the same parent structure (seenull_point_align()). Ifskip_point_alignmentis false, they will also have the same number of points (seealign_points()).- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) – The other mobject this mobject should be aligned to.
skip_point_alignment (bool) – Controls whether or not the computationally expensive point alignment is skipped (default: False).
- align_on_border(direction, buff=0.5)[source]#
Direction just needs to be a vector pointing towards side or corner in the 2d plane.
- align_to(mobject_or_point, direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Aligns mobject to another
Mobjectin a certain direction.Examples: mob1.align_to(mob2, UP) moves mob1 vertically so that its top edge lines ups with mob2’s top edge.
- Parameters
mobject_or_point (Mobject | np.ndarray | list) –
- property animate: _AnimationBuilder | T#
Used to animate the application of any method of
self.Any method called on
animateis converted to an animation of applying that method on the mobject itself.For example,
square.set_fill(WHITE)sets the fill color of a square, whilesquare.animate.set_fill(WHITE)animates this action.Multiple methods can be put in a single animation once via chaining:
self.play(my_mobject.animate.shift(RIGHT).rotate(PI))
Warning
Passing multiple animations for the same
Mobjectin one call toplay()is discouraged and will most likely not work properly. Instead of writing an animation likeself.play(my_mobject.animate.shift(RIGHT), my_mobject.animate.rotate(PI))
make use of method chaining.
Keyword arguments that can be passed to
Scene.play()can be passed directly after accessing.animate, like so:self.play(my_mobject.animate(rate_func=linear).shift(RIGHT))
This is especially useful when animating simultaneous
.animatecalls that you want to behave differently:self.play( mobject1.animate(run_time=2).rotate(PI), mobject2.animate(rate_func=there_and_back).shift(RIGHT), )
See also
Examples
Example: AnimateExample ¶
from manim import * class AnimateExample(Scene): def construct(self): s = Square() self.play(Create(s)) self.play(s.animate.shift(RIGHT)) self.play(s.animate.scale(2)) self.play(s.animate.rotate(PI / 2)) self.play(Uncreate(s))
Example: AnimateChainExample ¶
from manim import * class AnimateChainExample(Scene): def construct(self): s = Square() self.play(Create(s)) self.play(s.animate.shift(RIGHT).scale(2).rotate(PI / 2)) self.play(Uncreate(s))
Example: AnimateWithArgsExample ¶
from manim import * class AnimateWithArgsExample(Scene): def construct(self): s = Square() c = Circle() VGroup(s, c).arrange(RIGHT, buff=2) self.add(s, c) self.play( s.animate(run_time=2).rotate(PI / 2), c.animate(rate_func=there_and_back).shift(RIGHT), )
Warning
.animatewill interpolate the
Mobjectbetween its points prior to.animateand its points after applying.animateto it. This may result in unexpected behavior when attempting to interpolate along paths, or rotations. If you want animations to consider the points between, consider usingValueTrackerwith updaters instead.
- classmethod animation_override_for(animation_class)[source]#
Returns the function defining a specific animation override for this class.
- apply_complex_function(function, **kwargs)[source]#
Applies a complex function to a
Mobject. The x and y coordinates correspond to the real and imaginary parts respectively.Example
Example: ApplyFuncExample ¶
from manim import * class ApplyFuncExample(Scene): def construct(self): circ = Circle().scale(1.5) circ_ref = circ.copy() circ.apply_complex_function( lambda x: np.exp(x*1j) ) t = ValueTracker(0) circ.add_updater( lambda x: x.become(circ_ref.copy().apply_complex_function( lambda x: np.exp(x+t.get_value()*1j) )).set_color(BLUE) ) self.add(circ_ref) self.play(TransformFromCopy(circ_ref, circ)) self.play(t.animate.set_value(TAU), run_time=3)
- apply_to_family(func)[source]#
Apply a function to
selfand every submobject with points recursively.- Parameters
func (Callable[[Mobject], None]) – The function to apply to each mobject.
funcgets passed the respective (sub)mobject as parameter.- Returns
self- Return type
See also
family_members_with_points()
- arrange(direction=array([1., 0., 0.]), buff=0.25, center=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Sorts
Mobjectnext to each other on screen.Examples
Example: Example ¶
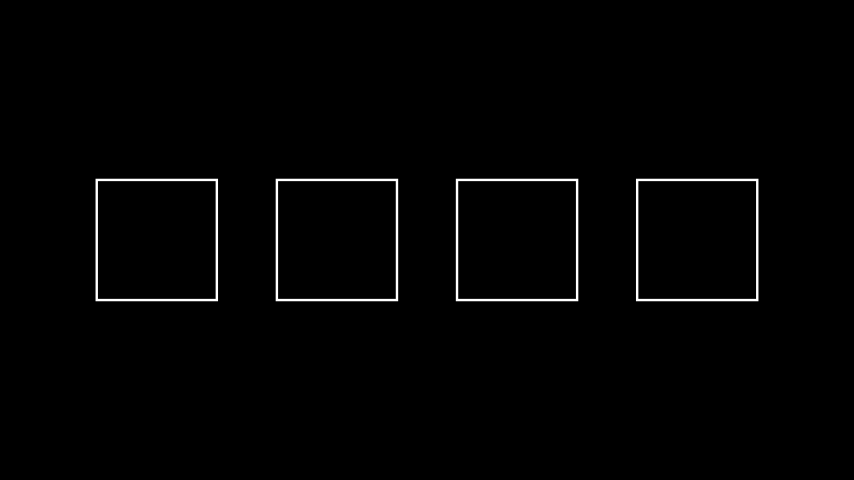
from manim import * class Example(Scene): def construct(self): s1 = Square() s2 = Square() s3 = Square() s4 = Square() x = VGroup(s1, s2, s3, s4).set_x(0).arrange(buff=1.0) self.add(x)
- Parameters
direction (Sequence[float]) –
- arrange_in_grid(rows=None, cols=None, buff=0.25, cell_alignment=array([0., 0., 0.]), row_alignments=None, col_alignments=None, row_heights=None, col_widths=None, flow_order='rd', **kwargs)[source]#
Arrange submobjects in a grid.
- Parameters
rows (int | None) – The number of rows in the grid.
cols (int | None) – The number of columns in the grid.
buff (float | tuple[float, float]) – The gap between grid cells. To specify a different buffer in the horizontal and vertical directions, a tuple of two values can be given -
(row, col).cell_alignment (np.ndarray) – The way each submobject is aligned in its grid cell.
row_alignments (str | None) – The vertical alignment for each row (top to bottom). Accepts the following characters:
"u"- up,"c"- center,"d"- down.col_alignments (str | None) – The horizontal alignment for each column (left to right). Accepts the following characters
"l"- left,"c"- center,"r"- right.row_heights (Iterable[float | None] | None) – Defines a list of heights for certain rows (top to bottom). If the list contains
None, the corresponding row will fit its height automatically based on the highest element in that row.col_widths (Iterable[float | None] | None) – Defines a list of widths for certain columns (left to right). If the list contains
None, the corresponding column will fit its width automatically based on the widest element in that column.flow_order (str) – The order in which submobjects fill the grid. Can be one of the following values: “rd”, “dr”, “ld”, “dl”, “ru”, “ur”, “lu”, “ul”. (“rd” -> fill rightwards then downwards)
- Returns
self- Return type
- Raises
ValueError – If
rowsandcolsare too small to fit all submobjects.ValueError – If
cols,col_alignmentsandcol_widthsorrows,row_alignmentsandrow_heightshave mismatching sizes.
Notes
If only one of
colsandrowsis set implicitly, the other one will be chosen big enough to fit all submobjects. If neither is set, they will be chosen to be about the same, tending towardscols>rows(simply because videos are wider than they are high).If both
cell_alignmentandrow_alignments/col_alignmentsare defined, the latter has higher priority.Examples
Example: ExampleBoxes ¶
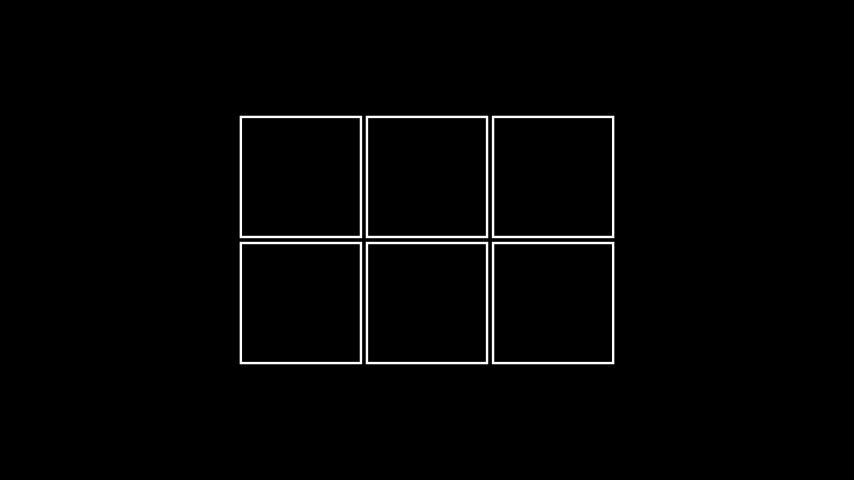
from manim import * class ExampleBoxes(Scene): def construct(self): boxes=VGroup(*[Square() for s in range(0,6)]) boxes.arrange_in_grid(rows=2, buff=0.1) self.add(boxes)
Example: ArrangeInGrid ¶
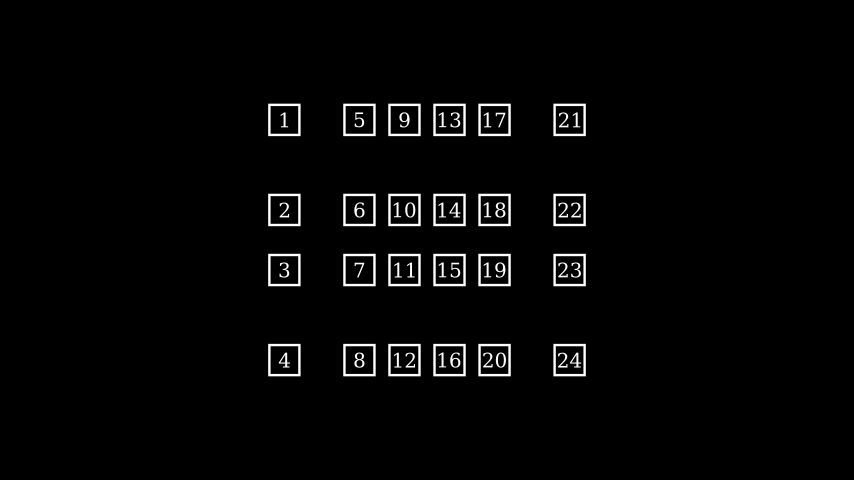
from manim import * class ArrangeInGrid(Scene): def construct(self): boxes = VGroup(*[ Rectangle(WHITE, 0.5, 0.5).add(Text(str(i+1)).scale(0.5)) for i in range(24) ]) self.add(boxes) boxes.arrange_in_grid( buff=(0.25,0.5), col_alignments="lccccr", row_alignments="uccd", col_widths=[1, *[None]*4, 1], row_heights=[1, None, None, 1], flow_order="dr" )
- arrange_submobjects(*args, **kwargs)[source]#
Arrange the position of
submobjectswith a small buffer.Examples
Example: ArrangeSumobjectsExample ¶
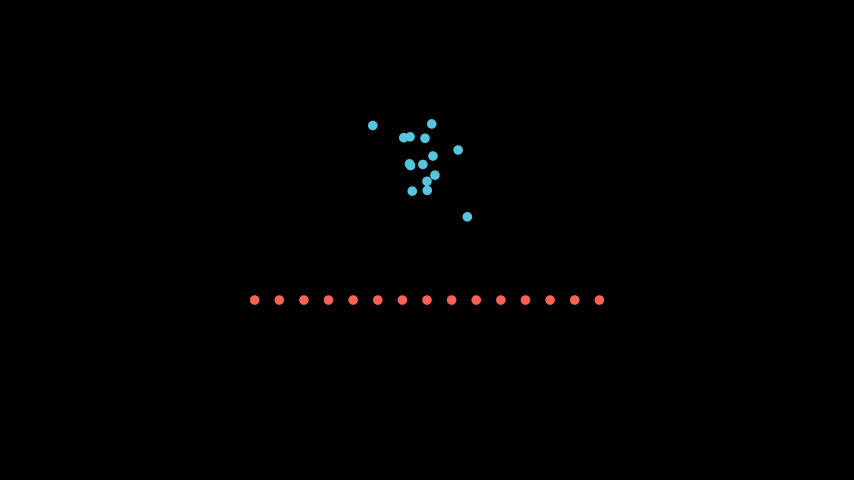
from manim import * class ArrangeSumobjectsExample(Scene): def construct(self): s= VGroup(*[Dot().shift(i*0.1*RIGHT*np.random.uniform(-1,1)+UP*np.random.uniform(-1,1)) for i in range(0,15)]) s.shift(UP).set_color(BLUE) s2= s.copy().set_color(RED) s2.arrange_submobjects() s2.shift(DOWN) self.add(s,s2)
- become(mobject, copy_submobjects=True, match_height=False, match_width=False, match_depth=False, match_center=False, stretch=False)[source]#
Edit points, colors and submobjects to be identical to another
MobjectNote
If both match_height and match_width are
Truethen the transformedMobjectwill match the height first and then the width- Parameters
match_height (bool) – If
True, then the transformedMobjectwill match the height of the originalmatch_width (bool) – If
True, then the transformedMobjectwill match the width of the originalmatch_depth (bool) – If
True, then the transformedMobjectwill match the depth of the originalmatch_center (bool) – If
True, then the transformedMobjectwill match the center of the originalstretch (bool) – If
True, then the transformedMobjectwill stretch to fit the proportions of the originalmobject (Mobject) –
copy_submobjects (bool) –
Examples
Example: BecomeScene ¶
from manim import * class BecomeScene(Scene): def construct(self): circ = Circle(fill_color=RED, fill_opacity=0.8) square = Square(fill_color=BLUE, fill_opacity=0.2) self.add(circ) self.wait(0.5) circ.become(square) self.wait(0.5)
- clear_updaters(recursive=True)[source]#
Remove every updater.
- Parameters
recursive (bool) – Whether to recursively call
clear_updaterson all submobjects.- Returns
self- Return type
See also
- copy()[source]#
Create and return an identical copy of the
Mobjectincluding allsubmobjects.- Returns
The copy.
- Return type
- Parameters
self (T) –
Note
The clone is initially not visible in the Scene, even if the original was.
- property depth#
The depth of the mobject.
- Return type
float
See also
- flip(axis=array([0., 1., 0.]), **kwargs)[source]#
Flips/Mirrors an mobject about its center.
Examples
Example: FlipExample ¶
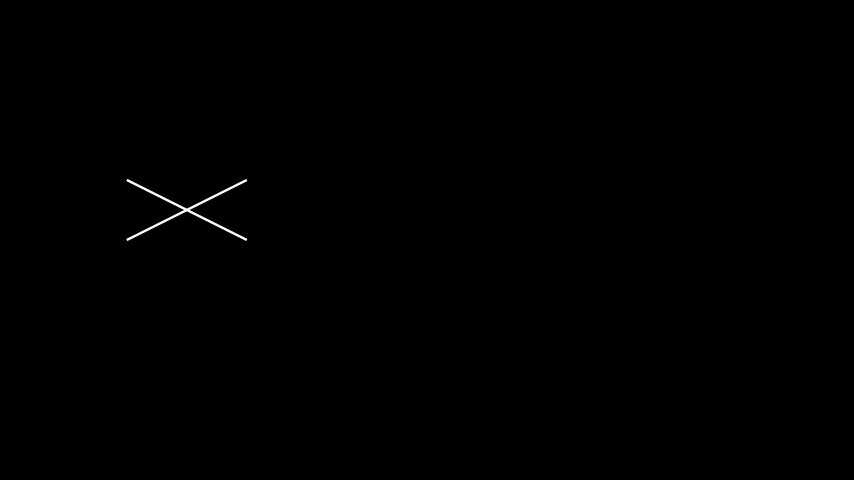
from manim import * class FlipExample(Scene): def construct(self): s= Line(LEFT, RIGHT+UP).shift(4*LEFT) self.add(s) s2= s.copy().flip() self.add(s2)
- generate_points()[source]#
Initializes
pointsand therefore the shape.Gets called upon creation. This is an empty method that can be implemented by subclasses.
- get_all_points()[source]#
Return all points from this mobject and all submobjects.
May contain duplicates; the order is in a depth-first (pre-order) traversal of the submobjects.
- Return type
ndarray
- get_critical_point(direction)[source]#
Picture a box bounding the
Mobject. Such a box has 9 ‘critical points’: 4 corners, 4 edge center, the center. This returns one of them, along the given direction.sample = Arc(start_angle=PI/7, angle = PI/5) # These are all equivalent max_y_1 = sample.get_top()[1] max_y_2 = sample.get_critical_point(UP)[1] max_y_3 = sample.get_extremum_along_dim(dim=1, key=1)
- get_merged_array(array_attr)[source]#
Return all of a given attribute from this mobject and all submobjects.
May contain duplicates; the order is in a depth-first (pre-order) traversal of the submobjects.
- Return type
ndarray
- get_midpoint()[source]#
Get coordinates of the middle of the path that forms the
Mobject.Examples
Example: AngleMidPoint ¶
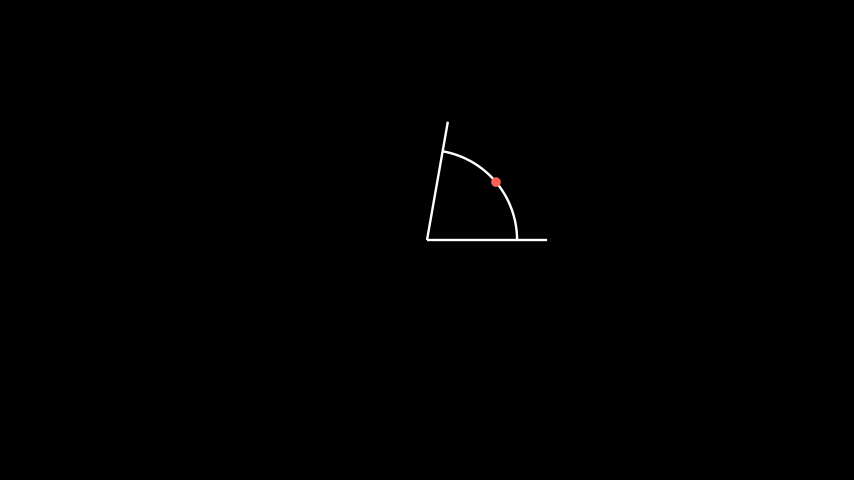
from manim import * class AngleMidPoint(Scene): def construct(self): line1 = Line(ORIGIN, 2*RIGHT) line2 = Line(ORIGIN, 2*RIGHT).rotate_about_origin(80*DEGREES) a = Angle(line1, line2, radius=1.5, other_angle=False) d = Dot(a.get_midpoint()).set_color(RED) self.add(line1, line2, a, d) self.wait()
- Return type
ndarray
- get_nadir()[source]#
Get nadir (opposite the zenith) coordinates of a box bounding a 3D
Mobject.- Return type
ndarray
- get_point_mobject(center=None)[source]#
The simplest
Mobjectto be transformed to or from self. Should by a point of the appropriate type
- get_time_based_updaters()[source]#
Return all updaters using the
dtparameter.The updaters use this parameter as the input for difference in time.
- Returns
The list of time based updaters.
- Return type
List[
Callable]
See also
- get_updaters()[source]#
Return all updaters.
- Returns
The list of updaters.
- Return type
List[
Callable]
See also
- get_x(direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Returns x coordinate of the center of the
Mobjectasfloat- Return type
float64
- get_y(direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Returns y coordinate of the center of the
Mobjectasfloat- Return type
float64
- get_z(direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Returns z coordinate of the center of the
Mobjectasfloat- Return type
float64
- has_time_based_updater()[source]#
Test if
selfhas a time based updater.- Returns
class –
Trueif at least one updater uses thedtparameter,Falseotherwise.- Return type
bool
See also
- property height#
The height of the mobject.
- Return type
float
Examples
Example: HeightExample ¶
from manim import * class HeightExample(Scene): def construct(self): decimal = DecimalNumber().to_edge(UP) rect = Rectangle(color=BLUE) rect_copy = rect.copy().set_stroke(GRAY, opacity=0.5) decimal.add_updater(lambda d: d.set_value(rect.height)) self.add(rect_copy, rect, decimal) self.play(rect.animate.set(height=5)) self.wait()
See also
- init_colors()[source]#
Initializes the colors.
Gets called upon creation. This is an empty method that can be implemented by subclasses.
- insert(index, mobject)[source]#
Inserts a mobject at a specific position into self.submobjects
Effectively just calls
self.submobjects.insert(index, mobject), whereself.submobjectsis a list.Highly adapted from
Mobject.add.- Parameters
index (int) – The index at which
mobject (Mobject) – The mobject to be inserted.
- interpolate(mobject1, mobject2, alpha, path_func=<function interpolate>)[source]#
Turns this
Mobjectinto an interpolation betweenmobject1andmobject2.Examples
Example: DotInterpolation ¶
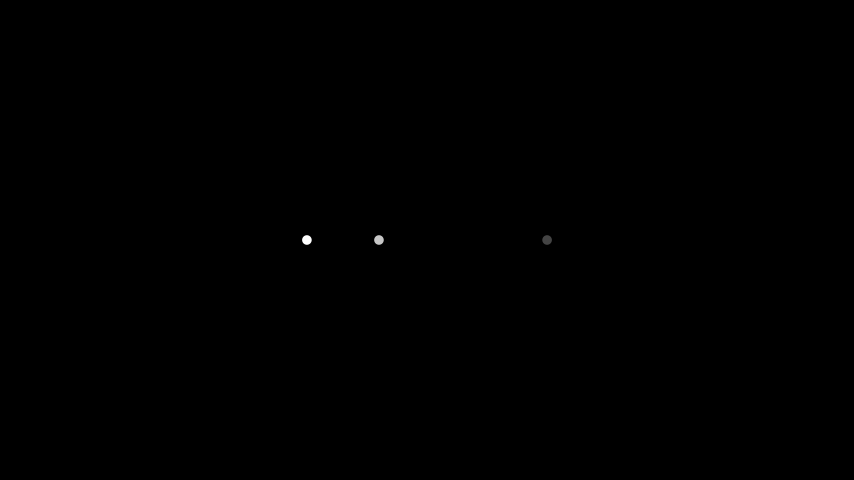
from manim import * class DotInterpolation(Scene): def construct(self): dotR = Dot(color=DARK_GREY) dotR.shift(2 * RIGHT) dotL = Dot(color=WHITE) dotL.shift(2 * LEFT) dotMiddle = VMobject().interpolate(dotL, dotR, alpha=0.3) self.add(dotL, dotR, dotMiddle)
- invert(recursive=False)[source]#
Inverts the list of
submobjects.- Parameters
recursive – If
True, all submobject lists of this mobject’s family are inverted.
Examples
Example: InvertSumobjectsExample ¶
from manim import * class InvertSumobjectsExample(Scene): def construct(self): s = VGroup(*[Dot().shift(i*0.1*RIGHT) for i in range(-20,20)]) s2 = s.copy() s2.invert() s2.shift(DOWN) self.play(Write(s), Write(s2))
- match_color(mobject)[source]#
Match the color with the color of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- match_coord(mobject, dim, direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Match the coordinates with the coordinates of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- match_depth(mobject, **kwargs)[source]#
Match the depth with the depth of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- match_dim_size(mobject, dim, **kwargs)[source]#
Match the specified dimension with the dimension of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- match_height(mobject, **kwargs)[source]#
Match the height with the height of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- match_points(mobject, copy_submobjects=True)[source]#
Edit points, positions, and submobjects to be identical to another
Mobject, while keeping the style unchanged.Examples
Example: MatchPointsScene ¶
from manim import * class MatchPointsScene(Scene): def construct(self): circ = Circle(fill_color=RED, fill_opacity=0.8) square = Square(fill_color=BLUE, fill_opacity=0.2) self.add(circ) self.wait(0.5) self.play(circ.animate.match_points(square)) self.wait(0.5)
- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
copy_submobjects (bool) –
- match_updaters(mobject)[source]#
Match the updaters of the given mobject.
- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) – The mobject whose updaters get matched.
- Returns
self- Return type
Note
All updaters from submobjects are removed, but only updaters of the given mobject are matched, not those of it’s submobjects.
See also
- match_width(mobject, **kwargs)[source]#
Match the width with the width of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- match_x(mobject, direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Match x coord. to the x coord. of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- match_y(mobject, direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Match y coord. to the x coord. of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- match_z(mobject, direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Match z coord. to the x coord. of another
Mobject.- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) –
- move_to(point_or_mobject, aligned_edge=array([0., 0., 0.]), coor_mask=array([1, 1, 1]))[source]#
Move center of the
Mobjectto certain coordinate.
- next_to(mobject_or_point, direction=array([1., 0., 0.]), buff=0.25, aligned_edge=array([0., 0., 0.]), submobject_to_align=None, index_of_submobject_to_align=None, coor_mask=array([1, 1, 1]))[source]#
Move this
Mobjectnext to another’sMobjector coordinate.Examples
Example: GeometricShapes ¶
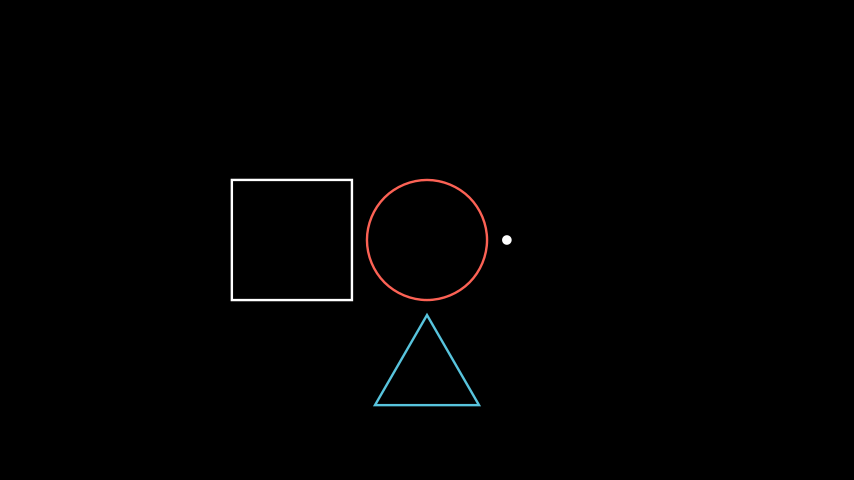
from manim import * class GeometricShapes(Scene): def construct(self): d = Dot() c = Circle() s = Square() t = Triangle() d.next_to(c, RIGHT) s.next_to(c, LEFT) t.next_to(c, DOWN) self.add(d, c, s, t)
- null_point_align(mobject)[source]#
If a
Mobjectwith points is being aligned to one without, treat both as groups, and push the one with points into its own submobjects list.
- reduce_across_dimension(reduce_func, dim)[source]#
Find the min or max value from a dimension across all points in this and submobjects.
- Parameters
dim (int) –
- Return type
float
- remove(*mobjects)[source]#
Remove
submobjects.The mobjects are removed from
submobjects, if they exist.Subclasses of mobject may implement
-and-=dunder methods.See also
- remove_updater(update_function)[source]#
Remove an updater.
If the same updater is applied multiple times, every instance gets removed.
- Parameters
update_function (Union[Callable[[Mobject], None], Callable[[Mobject, float], None]]) – The update function to be removed.
- Returns
self- Return type
See also
- restore()[source]#
Restores the state that was previously saved with
save_state().
- resume_updating(recursive=True)[source]#
Enable updating from updaters and animations.
- Parameters
recursive (bool) – Whether to recursively enable updating on all submobjects.
- Returns
self- Return type
See also
- rotate(angle, axis=array([0., 0., 1.]), about_point=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Rotates the
Mobjectabout a certain point.- Parameters
about_point (Sequence[float] | None) –
- rotate_about_origin(angle, axis=array([0., 0., 1.]), axes=[])[source]#
Rotates the
Mobjectabout the ORIGIN, which is at [0,0,0].
- save_state()[source]#
Save the current state (position, color & size). Can be restored with
restore().
- scale(scale_factor, **kwargs)[source]#
Scale the size by a factor.
Default behavior is to scale about the center of the mobject.
- Parameters
scale_factor (float) – The scaling factor \(\alpha\). If \(0 < |\alpha| < 1\), the mobject will shrink, and for \(|\alpha| > 1\) it will grow. Furthermore, if \(\alpha < 0\), the mobject is also flipped.
kwargs – Additional keyword arguments passed to
apply_points_function_about_point().
- Returns
self- Return type
Examples
Example: MobjectScaleExample ¶
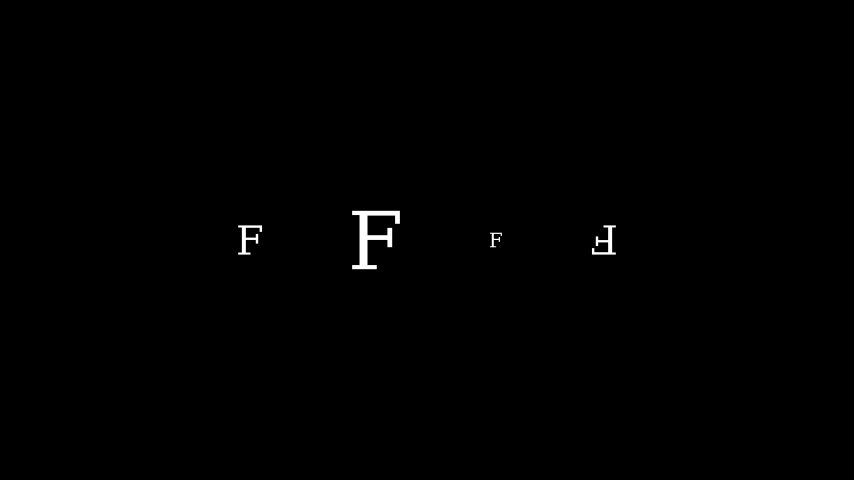
from manim import * class MobjectScaleExample(Scene): def construct(self): f1 = Text("F") f2 = Text("F").scale(2) f3 = Text("F").scale(0.5) f4 = Text("F").scale(-1) vgroup = VGroup(f1, f2, f3, f4).arrange(6 * RIGHT) self.add(vgroup)
See also
- scale_to_fit_depth(depth, **kwargs)[source]#
Scales the
Mobjectto fit a depth while keeping width/height proportional.
- scale_to_fit_height(height, **kwargs)[source]#
Scales the
Mobjectto fit a height while keeping width/depth proportional.- Returns
self- Return type
Examples
>>> from manim import * >>> sq = Square() >>> sq.width 2.0 >>> sq.scale_to_fit_height(5) Square >>> sq.height 5.0 >>> sq.width 5.0
- scale_to_fit_width(width, **kwargs)[source]#
Scales the
Mobjectto fit a width while keeping height/depth proportional.- Returns
self- Return type
Examples
>>> from manim import * >>> sq = Square() >>> sq.height 2.0 >>> sq.scale_to_fit_width(5) Square >>> sq.width 5.0 >>> sq.height 5.0
- set(**kwargs)[source]#
Sets attributes.
I.e.
my_mobject.set(foo=1)appliesmy_mobject.foo = 1.This is a convenience to be used along with
animateto animate setting attributes.In addition to this method, there is a compatibility layer that allows
get_*andset_*methods to get and set generic attributes. For instance:>>> mob = Mobject() >>> mob.set_foo(0) Mobject >>> mob.get_foo() 0 >>> mob.foo 0
This compatibility layer does not interfere with any
get_*orset_*methods that are explicitly defined.Warning
This compatibility layer is for backwards compatibility and is not guaranteed to stay around. Where applicable, please prefer getting/setting attributes normally or with the
set()method.- Parameters
**kwargs – The attributes and corresponding values to set.
- Returns
self- Return type
Examples
>>> mob = Mobject() >>> mob.set(foo=0) Mobject >>> mob.foo 0
- set_color(color='#FFFF00', family=True)[source]#
Condition is function which takes in one arguments, (x, y, z). Here it just recurses to submobjects, but in subclasses this should be further implemented based on the the inner workings of color
- Parameters
color (Color) –
family (bool) –
- classmethod set_default(**kwargs)[source]#
Sets the default values of keyword arguments.
If this method is called without any additional keyword arguments, the original default values of the initialization method of this class are restored.
- Parameters
kwargs – Passing any keyword argument will update the default values of the keyword arguments of the initialization function of this class.
Examples
>>> from manim import Square, GREEN >>> Square.set_default(color=GREEN, fill_opacity=0.25) >>> s = Square(); s.color, s.fill_opacity (<Color #83c167>, 0.25) >>> Square.set_default() >>> s = Square(); s.color, s.fill_opacity (<Color white>, 0.0)
Example: ChangedDefaultTextcolor ¶

from manim import * config.background_color = WHITE class ChangedDefaultTextcolor(Scene): def construct(self): Text.set_default(color=BLACK) self.add(Text("Changing default values is easy!")) # we revert the colour back to the default to prevent a bug in the docs. Text.set_default(color=WHITE)
- set_x(x, direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Set x value of the center of the
Mobject(intorfloat)
- set_y(y, direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Set y value of the center of the
Mobject(intorfloat)
- set_z(z, direction=array([0., 0., 0.]))[source]#
Set z value of the center of the
Mobject(intorfloat)
- set_z_index(z_index_value, family=True)[source]#
Sets the
Mobject’sz_indexto the value specified in z_index_value.- Parameters
z_index_value (float) – The new value of
z_indexset.family (bool) – If
True, thez_indexvalue of all submobjects is also set.
- Returns
The Mobject itself, after
z_indexis set. For chaining purposes. (Returns self.)- Return type
Examples
Example: SetZIndex ¶
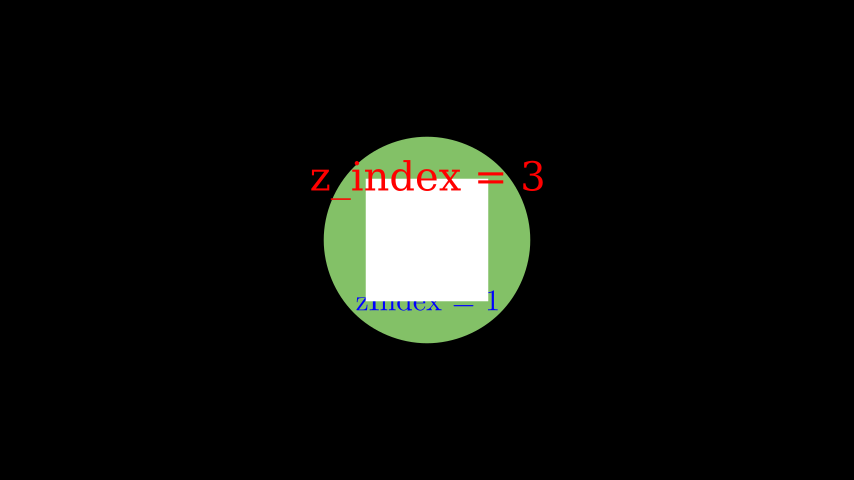
from manim import * class SetZIndex(Scene): def construct(self): text = Text('z_index = 3', color = PURE_RED).shift(UP).set_z_index(3) square = Square(2, fill_opacity=1).set_z_index(2) tex = Tex(r'zIndex = 1', color = PURE_BLUE).shift(DOWN).set_z_index(1) circle = Circle(radius = 1.7, color = GREEN, fill_opacity = 1) # z_index = 0 # Displaying order is now defined by z_index values self.add(text) self.add(square) self.add(tex) self.add(circle)
- set_z_index_by_z_coordinate()[source]#
Sets the
Mobject’s z coordinate to the value ofz_index.- Returns
The Mobject itself, after
z_indexis set. (Returns self.)- Return type
- shift(*vectors)[source]#
Shift by the given vectors.
- Parameters
vectors (ndarray) – Vectors to shift by. If multiple vectors are given, they are added together.
- Returns
self- Return type
See also
- shuffle(recursive=False)[source]#
Shuffles the list of
submobjects.
- shuffle_submobjects(*args, **kwargs)[source]#
Shuffles the order of
submobjectsExamples
Example: ShuffleSubmobjectsExample ¶
from manim import * class ShuffleSubmobjectsExample(Scene): def construct(self): s= VGroup(*[Dot().shift(i*0.1*RIGHT) for i in range(-20,20)]) s2= s.copy() s2.shuffle_submobjects() s2.shift(DOWN) self.play(Write(s), Write(s2))
- sort(point_to_num_func=<function Mobject.<lambda>>, submob_func=None)[source]#
Sorts the list of
submobjectsby a function defined bysubmob_func.
- sort_submobjects(*args, **kwargs)[source]#
Sort the
submobjects
- stretch_to_fit_depth(depth, **kwargs)[source]#
Stretches the
Mobjectto fit a depth, not keeping width/height proportional.
- stretch_to_fit_height(height, **kwargs)[source]#
Stretches the
Mobjectto fit a height, not keeping width/depth proportional.- Returns
self- Return type
Examples
>>> from manim import * >>> sq = Square() >>> sq.width 2.0 >>> sq.stretch_to_fit_height(5) Square >>> sq.height 5.0 >>> sq.width 2.0
- stretch_to_fit_width(width, **kwargs)[source]#
Stretches the
Mobjectto fit a width, not keeping height/depth proportional.- Returns
self- Return type
Examples
>>> from manim import * >>> sq = Square() >>> sq.height 2.0 >>> sq.stretch_to_fit_width(5) Square >>> sq.width 5.0 >>> sq.height 2.0
- suspend_updating(recursive=True)[source]#
Disable updating from updaters and animations.
- Parameters
recursive (bool) – Whether to recursively suspend updating on all submobjects.
- Returns
self- Return type
See also
- update(dt=0, recursive=True)[source]#
Apply all updaters.
Does nothing if updating is suspended.
- Parameters
dt (float) – The parameter
dtto pass to the update functions. Usually this is the time in seconds since the last call ofupdate.recursive (bool) – Whether to recursively update all submobjects.
- Returns
self- Return type
See also
- property width#
The width of the mobject.
- Return type
float
Examples
Example: WidthExample ¶
from manim import * class WidthExample(Scene): def construct(self): decimal = DecimalNumber().to_edge(UP) rect = Rectangle(color=BLUE) rect_copy = rect.copy().set_stroke(GRAY, opacity=0.5) decimal.add_updater(lambda d: d.set_value(rect.width)) self.add(rect_copy, rect, decimal) self.play(rect.animate.set(width=7)) self.wait()
See also