Axes#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.graphing.coordinate\_systems.Axes
- class Axes(x_range=None, y_range=None, x_length=12, y_length=6, axis_config=None, x_axis_config=None, y_axis_config=None, tips=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
VGroup,CoordinateSystemCreates a set of axes.
- Parameters
x_range (Sequence[float] | None) – The
(x_min, x_max, x_step)values of the x-axis.y_range (Sequence[float] | None) – The
(y_min, y_max, y_step)values of the y-axis.x_length (float | None) – The length of the x-axis.
y_length (float | None) – The length of the y-axis.
axis_config (dict | None) – Arguments to be passed to
NumberLinethat influences both axes.x_axis_config (dict | None) – Arguments to be passed to
NumberLinethat influence the x-axis.y_axis_config (dict | None) – Arguments to be passed to
NumberLinethat influence the y-axis.tips (bool) – Whether or not to include the tips on both axes.
kwargs – Additional arguments to be passed to
CoordinateSystemandVGroup.
Examples
Example: LogScalingExample ¶
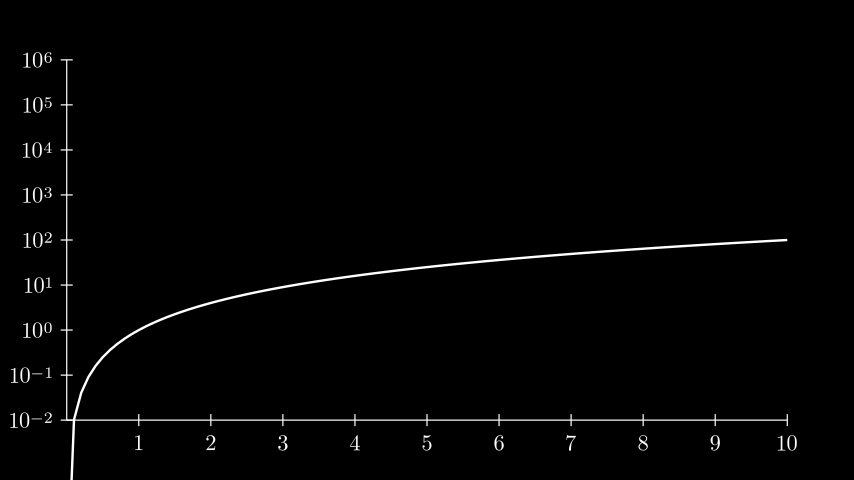
from manim import * class LogScalingExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes( x_range=[0, 10, 1], y_range=[-2, 6, 1], tips=False, axis_config={"include_numbers": True}, y_axis_config={"scaling": LogBase(custom_labels=True)}, ) # x_min must be > 0 because log is undefined at 0. graph = ax.plot(lambda x: x ** 2, x_range=[0.001, 10], use_smoothing=False) self.add(ax, graph)
Styling arguments can be passed to the underlying
NumberLinemobjects that represent the axes:Example: AxesWithDifferentTips ¶
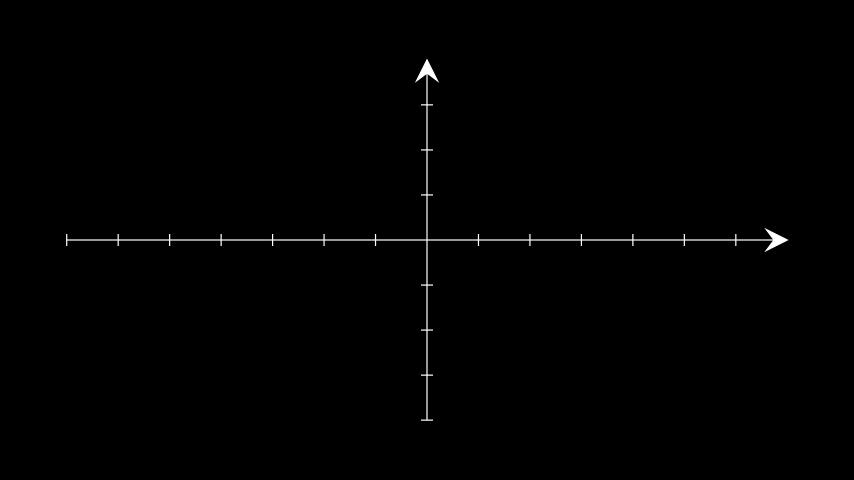
from manim import * class AxesWithDifferentTips(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(axis_config={'tip_shape': StealthTip}) self.add(ax)
Methods
Accepts coordinates from the axes and returns a point with respect to the scene.
Gets the axes.
Defines labels for the x-axis and y-axis of the graph.
Draws a line graph.
Accepts a point from the scene and returns its coordinates with respect to the axes.
Attributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridescolordepthThe depth of the mobject.
fill_colorIf there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorwidthThe width of the mobject.
- coords_to_point(*coords)[source]#
Accepts coordinates from the axes and returns a point with respect to the scene.
- Parameters
coords (float | Sequence[float] | Sequence[Sequence[float]] | np.ndarray) –
The coordinates. Each coord is passed as a separate argument:
ax.coords_to_point(1, 2, 3).Also accepts a list of coordinates
ax.coords_to_point( [x_0, x_1, ...], [y_0, y_1, ...], ... )ax.coords_to_point( [[x_0, y_0, z_0], [x_1, y_1, z_1]] )- Returns
A point with respect to the scene’s coordinate system. The shape of the array will be similar to the shape of the input.
- Return type
np.ndarray
Examples
>>> from manim import Axes >>> import numpy as np >>> ax = Axes() >>> np.around(ax.coords_to_point(1, 0, 0), 2) array([0.86, 0. , 0. ]) >>> np.around(ax.coords_to_point([[0, 1], [1, 1], [1, 0]]), 2) array([[0. , 0.75, 0. ], [0.86, 0.75, 0. ], [0.86, 0. , 0. ]]) >>> np.around( ... ax.coords_to_point([0, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0]), 2 ... ) # Transposed version of the above array([[0. , 0.86, 0.86], [0.75, 0.75, 0. ], [0. , 0. , 0. ]])
Example: CoordsToPointExample ¶
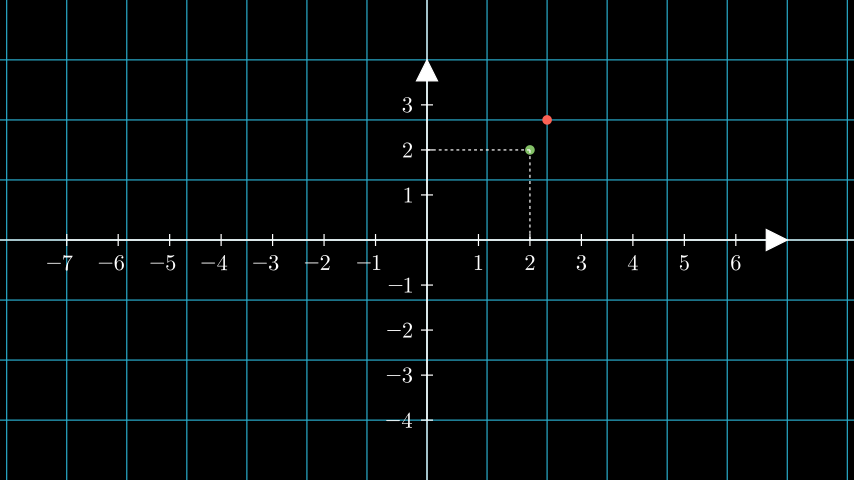
from manim import * class CoordsToPointExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes().add_coordinates() # a dot with respect to the axes dot_axes = Dot(ax.coords_to_point(2, 2), color=GREEN) lines = ax.get_lines_to_point(ax.c2p(2,2)) # a dot with respect to the scene # the default plane corresponds to the coordinates of the scene. plane = NumberPlane() dot_scene = Dot((2,2,0), color=RED) self.add(plane, dot_scene, ax, dot_axes, lines)
- get_axis_labels(x_label='x', y_label='y')[source]#
Defines labels for the x-axis and y-axis of the graph.
For increased control over the position of the labels, use
get_x_axis_label()andget_y_axis_label().- Parameters
- Returns
A
VGroupof the labels for the x_axis and y_axis.- Return type
See also
Examples
Example: GetAxisLabelsExample ¶
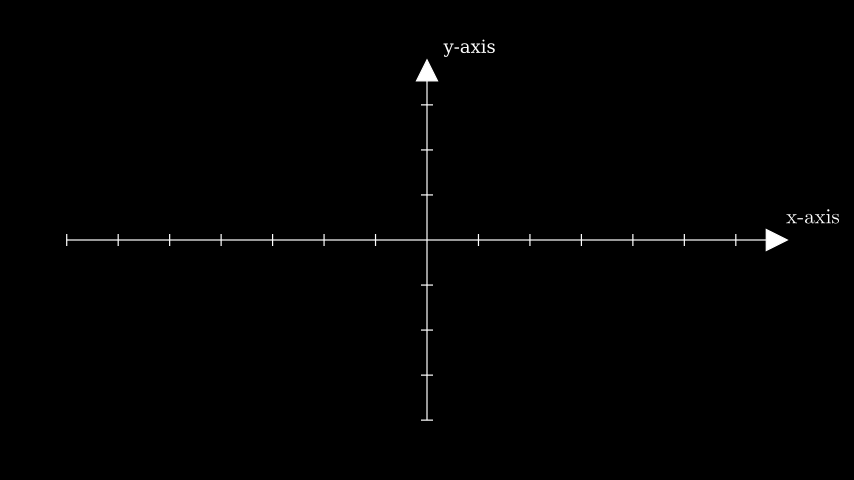
from manim import * class GetAxisLabelsExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() labels = ax.get_axis_labels( Tex("x-axis").scale(0.7), Text("y-axis").scale(0.45) ) self.add(ax, labels)
- plot_line_graph(x_values, y_values, z_values=None, line_color='#FFFF00', add_vertex_dots=True, vertex_dot_radius=0.08, vertex_dot_style=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Draws a line graph.
The graph connects the vertices formed from zipping
x_values,y_valuesandz_values. Also addsDotsat the vertices ifadd_vertex_dotsis set toTrue.- Parameters
x_values (Iterable[float]) – Iterable of values along the x-axis.
y_values (Iterable[float]) – Iterable of values along the y-axis.
z_values (Iterable[float] | None) – Iterable of values (zeros if z_values is None) along the z-axis.
line_color (Color) – Color for the line graph.
add_vertex_dots (bool) – Whether or not to add
Dotat each vertex.vertex_dot_radius (float) – Radius for the
Dotat each vertex.vertex_dot_style (dict | None) – Style arguments to be passed into
Dotat each vertex.kwargs – Additional arguments to be passed into
VMobject.
- Returns
A VDict containing both the line and dots (if specified). The line can be accessed with:
line_graph["line_graph"]. The dots can be accessed with:line_graph["vertex_dots"].- Return type
Examples
Example: LineGraphExample ¶
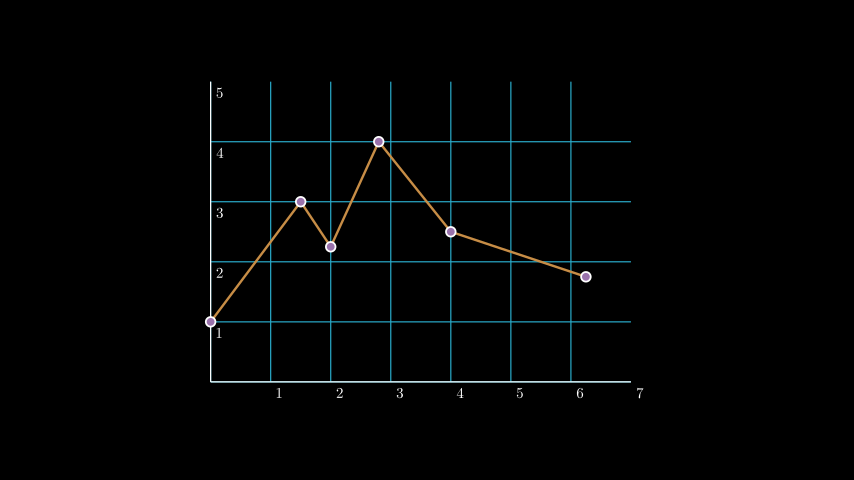
from manim import * class LineGraphExample(Scene): def construct(self): plane = NumberPlane( x_range = (0, 7), y_range = (0, 5), x_length = 7, axis_config={"include_numbers": True}, ) plane.center() line_graph = plane.plot_line_graph( x_values = [0, 1.5, 2, 2.8, 4, 6.25], y_values = [1, 3, 2.25, 4, 2.5, 1.75], line_color=GOLD_E, vertex_dot_style=dict(stroke_width=3, fill_color=PURPLE), stroke_width = 4, ) self.add(plane, line_graph)
- point_to_coords(point)[source]#
Accepts a point from the scene and returns its coordinates with respect to the axes.
- Parameters
point (Sequence[float]) – The point, i.e.
RIGHTor[0, 1, 0]. Also accepts a list of points as[RIGHT, [0, 1, 0]].- Returns
The coordinates on the axes, i.e.
[4.0, 7.0]. Or a list of coordinates if point is a list of points.- Return type
np.ndarray[float]
Examples
>>> from manim import Axes, RIGHT >>> import numpy as np >>> ax = Axes(x_range=[0, 10, 2]) >>> np.around(ax.point_to_coords(RIGHT), 2) array([5.83, 0. ]) >>> np.around(ax.point_to_coords([[0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0]]), 2) array([[5. , 0. ], [5.83, 0. ]])
Example: PointToCoordsExample ¶
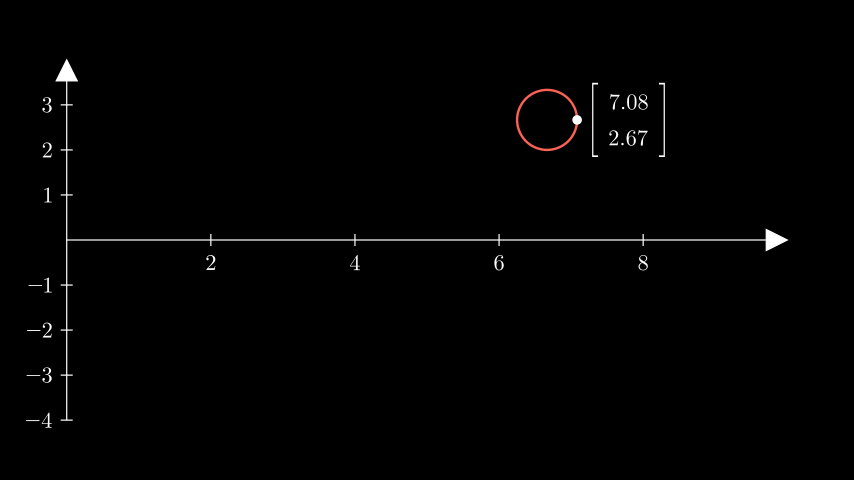
from manim import * class PointToCoordsExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(x_range=[0, 10, 2]).add_coordinates() circ = Circle(radius=0.5).shift(UR * 2) # get the coordinates of the circle with respect to the axes coords = np.around(ax.point_to_coords(circ.get_right()), decimals=2) label = ( Matrix([[coords[0]], [coords[1]]]).scale(0.75).next_to(circ, RIGHT) ) self.add(ax, circ, label, Dot(circ.get_right()))