Brace#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.svg.brace.Brace
- class Brace(mobject, direction=array([0., - 1., 0.]), buff=0.2, sharpness=2, stroke_width=0, fill_opacity=1.0, background_stroke_width=0, background_stroke_color='#000000', **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
VMobjectFromSVGPathTakes a mobject and draws a brace adjacent to it.
Passing a direction vector determines the direction from which the brace is drawn. By default it is drawn from below.
- Parameters
mobject (Mobject) – The mobject adjacent to which the brace is placed.
direction (Sequence[float] | None) – The direction from which the brace faces the mobject.
See also
Examples
Example: BraceExample ¶
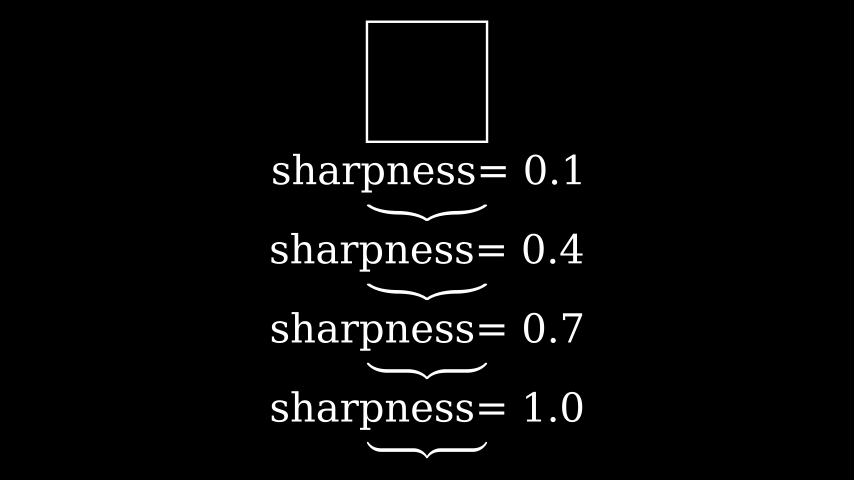
from manim import * class BraceExample(Scene): def construct(self): s = Square() self.add(s) for i in np.linspace(0.1,1.0,4): br = Brace(s, sharpness=i) t = Text(f"sharpness= {i}").next_to(br, RIGHT) self.add(t) self.add(br) VGroup(*self.mobjects).arrange(DOWN, buff=0.2)
Methods
Uses
shoelace_direction()to calculate the direction.get_texget_textget_tipput_at_tipAttributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridescolordepthThe depth of the mobject.
fill_colorIf there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorwidthThe width of the mobject.
- get_direction()[source]#
Uses
shoelace_direction()to calculate the direction. The direction of points determines in which direction the object is drawn, clockwise or counterclockwise.Examples
The default direction of a
Circleis counterclockwise:>>> from manim import Circle >>> Circle().get_direction() 'CCW'
- Returns
Either
"CW"or"CCW".- Return type
str