Arrow#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.geometry.line.Arrow
- class Arrow(*args, stroke_width=6, buff=0.25, max_tip_length_to_length_ratio=0.25, max_stroke_width_to_length_ratio=5, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
LineAn arrow.
- Parameters
args (Any) – Arguments to be passed to
Line.stroke_width (float) – The thickness of the arrow. Influenced by
max_stroke_width_to_length_ratio.buff (float) – The distance of the arrow from its start and end points.
max_tip_length_to_length_ratio (float) –
tip_lengthscales with the length of the arrow. Increasing this ratio raises the max value oftip_length.max_stroke_width_to_length_ratio (float) –
stroke_widthscales with the length of the arrow. Increasing this ratio ratios the max value ofstroke_width.kwargs – Additional arguments to be passed to
Line.
See also
ArrowTipCurvedArrowExamples
Example: ArrowExample ¶
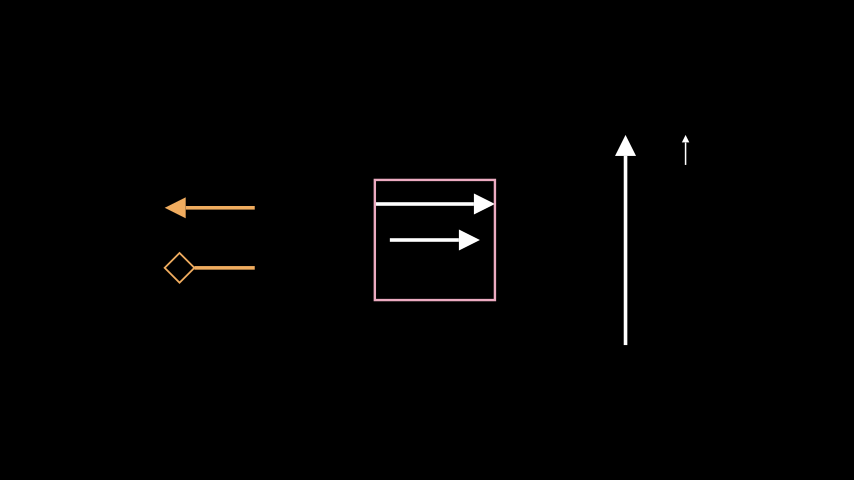
from manim import * from manim.mobject.geometry.tips import ArrowSquareTip class ArrowExample(Scene): def construct(self): arrow_1 = Arrow(start=RIGHT, end=LEFT, color=GOLD) arrow_2 = Arrow(start=RIGHT, end=LEFT, color=GOLD, tip_shape=ArrowSquareTip).shift(DOWN) g1 = Group(arrow_1, arrow_2) # the effect of buff square = Square(color=MAROON_A) arrow_3 = Arrow(start=LEFT, end=RIGHT) arrow_4 = Arrow(start=LEFT, end=RIGHT, buff=0).next_to(arrow_1, UP) g2 = Group(arrow_3, arrow_4, square) # a shorter arrow has a shorter tip and smaller stroke width arrow_5 = Arrow(start=ORIGIN, end=config.top).shift(LEFT * 4) arrow_6 = Arrow(start=config.top + DOWN, end=config.top).shift(LEFT * 3) g3 = Group(arrow_5, arrow_6) self.add(Group(g1, g2, g3).arrange(buff=2))
Example: ArrowExample ¶
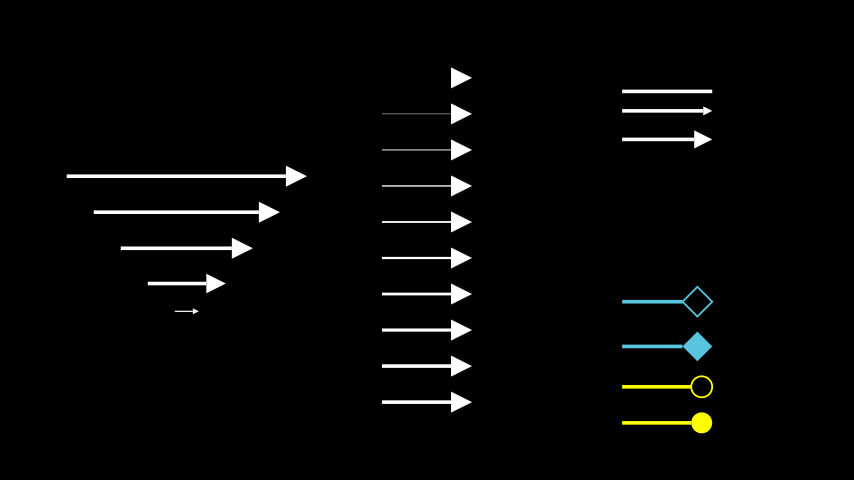
from manim import * class ArrowExample(Scene): def construct(self): left_group = VGroup() # As buff increases, the size of the arrow decreases. for buff in np.arange(0, 2.2, 0.45): left_group += Arrow(buff=buff, start=2 * LEFT, end=2 * RIGHT) # Required to arrange arrows. left_group.arrange(DOWN) left_group.move_to(4 * LEFT) middle_group = VGroup() # As max_stroke_width_to_length_ratio gets bigger, # the width of stroke increases. for i in np.arange(0, 5, 0.5): middle_group += Arrow(max_stroke_width_to_length_ratio=i) middle_group.arrange(DOWN) UR_group = VGroup() # As max_tip_length_to_length_ratio increases, # the length of the tip increases. for i in np.arange(0, 0.3, 0.1): UR_group += Arrow(max_tip_length_to_length_ratio=i) UR_group.arrange(DOWN) UR_group.move_to(4 * RIGHT + 2 * UP) DR_group = VGroup() DR_group += Arrow(start=LEFT, end=RIGHT, color=BLUE, tip_shape=ArrowSquareTip) DR_group += Arrow(start=LEFT, end=RIGHT, color=BLUE, tip_shape=ArrowSquareFilledTip) DR_group += Arrow(start=LEFT, end=RIGHT, color=YELLOW, tip_shape=ArrowCircleTip) DR_group += Arrow(start=LEFT, end=RIGHT, color=YELLOW, tip_shape=ArrowCircleFilledTip) DR_group.arrange(DOWN) DR_group.move_to(4 * RIGHT + 2 * DOWN) self.add(left_group, middle_group, UR_group, DR_group)
Methods
Returns the default tip_length of the arrow.
Returns the normal of a vector.
Resets the normal of a vector
Scale an arrow, but keep stroke width and arrow tip size fixed.
Attributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridescolordepthThe depth of the mobject.
fill_colorIf there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorwidthThe width of the mobject.
- get_default_tip_length()[source]#
Returns the default tip_length of the arrow.
Examples
>>> Arrow().get_default_tip_length() 0.35
- Return type
float
- get_normal_vector()[source]#
Returns the normal of a vector.
Examples
>>> np.round(Arrow().get_normal_vector()) + 0. # add 0. to avoid negative 0 in output array([ 0., 0., -1.])
- Return type
ndarray
- scale(factor, scale_tips=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Scale an arrow, but keep stroke width and arrow tip size fixed.
See also
Examples
>>> arrow = Arrow(np.array([-1, -1, 0]), np.array([1, 1, 0]), buff=0) >>> scaled_arrow = arrow.scale(2) >>> np.round(scaled_arrow.get_start_and_end(), 8) + 0 array([[-2., -2., 0.], [ 2., 2., 0.]]) >>> arrow.tip.length == scaled_arrow.tip.length True
Manually scaling the object using the default method
scale()does not have the same properties:>>> new_arrow = Arrow(np.array([-1, -1, 0]), np.array([1, 1, 0]), buff=0) >>> another_scaled_arrow = VMobject.scale(new_arrow, 2) >>> another_scaled_arrow.tip.length == arrow.tip.length False